Angiotensin II stimulates phosphorylation of an ectodomain-truncated platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta and its binding to class IA PI3K in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 16569213
- PMCID: PMC1513282
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060095
Angiotensin II stimulates phosphorylation of an ectodomain-truncated platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta and its binding to class IA PI3K in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
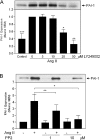
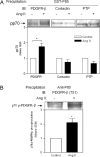
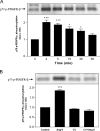
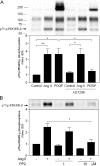
PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) activity is involved in Ang (angiotensin) II-stimulated VSMC (vascular smooth muscle cell) growth and hypertrophy. In the present study, we demonstrate that the inhibition of PI3K in VSMCs by expression of a dominant-negative p85alpha mutant lacking the p110-binding domain (Deltap85), or by treatment of cells with LY294002, inhibited Ang II-stimulated PAI-1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) mRNA expression. Using a GST (glutathione S-transferase) fusion protein containing the p85 N-terminal SH2 (Src homology 2) domain as 'bait' followed by MS/MS (tandem MS), we identified a 70 kDa fragment of the p70 PDGFR-beta (platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta) as a signalling adapter that is phosphorylated and recruits the p85 subunit of PI3K after Ang II stimulation of AT1 (Ang II subtype 1) receptors on VSMCs. This fragment of the PDGFR-beta, which has a truncation of its extracellular domain, accounted for approx. 15% of the total PDGFR-beta detected in VSMCs with an antibody against its cytoplasmic domain. Stimulation of VSMCs with Ang II increased tyrosine-phosphorylation of p70 PDGFR-beta at Tyr751 and Tyr1021 and increased its binding to p85. PDGF also induced phosphorylation of p70 PDGFR-beta, a response inhibited by the PDGF tyrosine kinase selective inhibitor, AG1296. By contrast, Ang II-induced phosphorylation of the 70 kDa receptor was not affected by AG1296. Ang II-stimulated phosphorylation of the p70 PDGFR-beta was blocked by the AT1 receptor antagonist, candesartan (CV 11974) and was partially inhibited by PP2 {4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine}, an Src family kinase inhibitor. Our result suggests that the p70 PDGFR-beta functions as an adapter that recruits PI3K to the membrane upon AT1 receptor stimulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II regulation of the Na+ pump involves the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells.Endocrinology. 2004 Mar;145(3):1151-60. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0100. Epub 2003 Nov 20. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 14630723
-
SAM68: a downstream target of angiotensin II signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells in genetic hypertension.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004 May;286(5):H1954-62. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00134.2003. Epub 2003 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14693677
-
Angiotensin II-induced growth of vascular smooth muscle cells requires an Src-dependent activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor.Kidney Int. 2000 Aug;58(2):549-58. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.t01-1-00201.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10916078
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor transactivation mediates the trophic effects of angiotensin II in vivo.Hypertension. 2004 Aug;44(2):195-202. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000132883.20764.12. Epub 2004 Jun 14. Hypertension. 2004. PMID: 15197170
-
The role of tyrosine phosphorylation in angiotensin II mediated intracellular signaling and cell growth.J Mol Med (Berl). 1996 Feb;74(2):85-91. doi: 10.1007/BF00196783. J Mol Med (Berl). 1996. PMID: 8820403 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Hypoxia-Mediated Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation Leading to Vascular Remodeling.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Dec 24;2022:3959845. doi: 10.1155/2022/3959845. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36593773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a novel phosphorylation site on TBC1D4 regulated by AMP-activated protein kinase in skeletal muscle.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):C377-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00297.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19923418 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II receptor type 1 blockade decreases CTGF/CCN2-mediated damage and fibrosis in normal and dystrophic skeletal muscles.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Apr;16(4):752-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01354.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21645240 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery remodeling and suppresses CREB depletion in arterial smooth muscle cells.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;62(6):539-48. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000014. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24084215 Free PMC article.
-
Connective tissue growth factor differentially binds to members of the cystine knot superfamily and potentiates platelet-derived growth factor-B signaling in rabbit corneal fibroblast cells.World J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 26;6(4):379-88. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.379. World J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26629321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eguchi S., Numaguchi K., Iwasaki H., Matsumoto T., Yamakawa T., Utsunomiya H., Motley E. D., Kawakatsu H., Owada K. M., Hirata Y., et al. Calcium-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates the angiotensin II-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:8890–8896. - PubMed
-
- Saward L., Zahradka P. Angiotensin II activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1997;81:249–257. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi T., Taniguchi T., Konishi H., Kikkawa U., Ishikawa Y., Yokoyama M. Activation of Akt/protein kinase B after stimulation with angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;276:H1927–H1934. - PubMed
-
- Cantley L. C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296:1655–1657. - PubMed
-
- Lokker N. A., O'Hare J. P., Barsoumian A., Tomlinson J. E., Ramakrishnan V., Fretto L. J., Giese N. A. Functional importance of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains. Identification of PDGF binding site and neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:33037–33044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

