Immune complexes from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid induce FcgammaRIIa dependent and rheumatoid factor correlated production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha by peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 16569263
- PMCID: PMC1526644
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1926
Immune complexes from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid induce FcgammaRIIa dependent and rheumatoid factor correlated production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha by peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
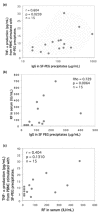
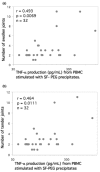
Immune complexes (ICs) can induce production of cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells via Fc receptors. Rheumatoid factor (RF) develop in response to ICs in many clinical and experimental settings. We investigated whether and how polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitated ICs from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) sera and synovial fluid (SF) can influence cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. We also examined the relationship between RF and IC induced cytokine production. Parallel sera and SF from 47 RA patients and sera from 15 healthy control individuals were PEG precipitated. The precipitates were added to serum-free peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha levels were measured after 20 hours. In separate cell culture experiments FcgammaRIIa and FcgammaRIII were blocked and monocytes were depleted or enriched. RF in serum was determined by nephelometry, and IgG levels in precipitates and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in serum were measured using ELISA. Clinical data were collected from the patients' charts. In two separate investigations, we demonstrated a correlation between RF, PEG-precipitated IgG levels and induction of the proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha by PEG-precipitated SF ICs. No such correlation was found for serum ICs. TNF-alpha levels induced by SF precipitates, but not serum precipitates, correlated with the number of swollen and tender joints. Monocytes/macrophages were shown to be the main responder cells, and blockade of FcgammaRIIa, but not blockade of FcgammaRIII, inhibited TNF-alpha production in cultures stimulated with precipitated ICs. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide correlated with RF but exhibited no association with IgG content in PEG precipitates or with precipitate-induced TNF-alpha levels. These findings support the hypothesis that SF ICs and correlated RF production are directly linked to cytokine-dependent inflammation in RA. Suppression of monocytes/macrophages in RA joints or blockade of the primate-specific activating FcgammaRIIa receptor might be ways to reduce IC-induced TNF-alpha production in the joints of seropositive RA patients.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Surface-bound anti-type II collagen-containing immune complexes induce production of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1beta, and interleukin-8 from peripheral blood monocytes via Fc gamma receptor IIA: a potential pathophysiologic mechanism for humoral anti-type II collagen immunity in arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Jun;54(6):1759-71. doi: 10.1002/art.21892. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16736518
-
Induction of macrophage secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha through Fcgamma receptor IIa engagement by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies to citrullinated proteins complexed with fibrinogen.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Mar;58(3):678-88. doi: 10.1002/art.23284. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18311806
-
High levels of osteoprotegerin and soluble receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand in serum of rheumatoid arthritis patients and their normalization after anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha treatment.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Jul;46(7):1744-53. doi: 10.1002/art.10388. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 12124857
-
B lymphocyte function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: impact of regulatory T lymphocytes and macrophages--modulation by antirheumatic drugs.Dan Med Bull. 1988 Apr;35(2):140-57. Dan Med Bull. 1988. PMID: 3282810 Review.
-
TNF alpha as a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis.Circ Shock. 1994 Aug;43(4):179-84. Circ Shock. 1994. PMID: 7895323 Review.
Cited by
-
A specific anti-citrullinated protein antibody profile identifies a group of rheumatoid arthritis patients with a toll-like receptor 4-mediated disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Oct 6;18(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1128-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27716430 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Proteomics Profiling for Biomarker Identification Among Patients Suffering With Indian Post Kala Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 27;10:251. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00251. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32528904 Free PMC article.
-
The Contribution of Macrophage Plasticity to Inflammatory Arthritis and Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets.Cells. 2024 Sep 20;13(18):1586. doi: 10.3390/cells13181586. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kawasaki Disease: The Role of Immune Complexes Revisited.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 12;10:1156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01156. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31263461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular pathways of structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jun;39(4):355-363. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0634-0. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 28597065 Review.
References
-
- Scott DL. Prognostic factors in early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000:24–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

