Real-time reverse transcription-PCR quantification of cytokine mRNA expression in golden Syrian hamster infected with Leishmania infantum and treated with a new amphotericin B formulation
- PMID: 16569829
- PMCID: PMC1426985
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1195-1201.2006
Real-time reverse transcription-PCR quantification of cytokine mRNA expression in golden Syrian hamster infected with Leishmania infantum and treated with a new amphotericin B formulation
Abstract
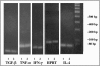
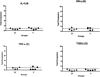
A real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR assay was developed for the quantification of cytokine mRNA expression in the golden Syrian hamster Mesocricetus auratus infected with Leishmania infantum and treated with amphotericin B (AMB) formulated in microspheres made of human serum albumin (HSA). Treatment was administered intravenously on days 69, 71, and 73 postinfection (p.i.) with 10(7) metacyclic promastigotes, at doses of 2 and 40 mg/kg of AMB. High infection levels were recorded for untreated animals by day 76 p.i., with parasite loads always about 2 log10 per gram higher in the liver than in the spleen. Treatment was highly effective with both doses, but at 40 mg/kg, almost complete parasite elimination was achieved. mRNA expression of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and, to a lesser extent, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in spleen cells was up-regulated in most animals of the untreated group. The mRNA expression of interleukin-4 was strongly down-regulated in untreated as well as treated infected animals. Treatment with the lower dose of AMB-HSA down-regulated the mRNA expression of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, with no effect on the deactivating cytokine TGF-beta. In contrast, treatment with the higher dose (40 mg/kg) of the formulation caused moderate up-regulation of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha and strong suppression of TGF-beta. Treatment of noninfected animals did not alter the cytokine expression pattern with regard to untreated controls. Our results suggest that treatment of L. infantum-infected Syrian hamsters with highly effective nontoxic doses of AMB-HSA causes deactivation of the anti-inflammatory cytokine TGF-beta, which in turn results in up-regulation of the Th1 cytokines IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha.
Figures

References
-
- Ashford, R. W. 1996. Leishmaniasis: reservoirs and their significance in control. Clin. Derm. 14:523-532. - PubMed
-
- Barral-Netto, M. A., A. Barral, C. E. Brownell, Y. A. Skeiky, L. R. Ellingsworth, D. R. Twardzik, and S. G. Reed. 1992. Transforming growth factor-β in leishmanial infections: a parasite escape mechanism. Science 257:545-548. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Wen, L., C. A. Rush, J. Tan, and G. J. Weil. 2004. Quantitative analysis of gender-regulated transcripts in the filarial nematode Brugia malayi by real-time RT-PCR. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 137:329-337. - PubMed
-
- Chia, J. K. S., and M. Pollack. 1989. Amphotericin B induces tumour necrosis factor production by murine macrophages. J. Infect. Dis. 159:113-116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

