Assessment of the paradoxical effect of caspofungin in therapy of candidiasis
- PMID: 16569843
- PMCID: PMC1426960
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1293-1297.2006
Assessment of the paradoxical effect of caspofungin in therapy of candidiasis
Erratum in
- Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jul;50(7):2592
Abstract
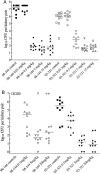
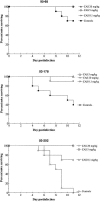
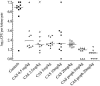
Paradoxical growth of some Candida albicans isolates in the presence of caspofungin (CAS) in vitro has been demonstrated previously. We sought to determine whether a similar phenomenon occurred in vivo. A systemic model of candidiasis was studied in CD-1 mice by intravenous inoculation of different isolates of C. albicans. Infected animals were treated with CAS at various dosages (0.01 to 20 mg/kg) and CFU remaining in the kidneys determined. Four clinical isolates that showed paradoxical growth in vitro and one that did not were tested. Recovery of CFU from the kidneys showed that dosages of CAS at 0.1 mg/kg and above were efficacious in the reduction of C. albicans, but were not curative. Against isolates that show paradoxical growth in vitro, CAS was efficacious, but lacked dose responsiveness above 0.5 mg/kg against three of the four. One isolate, 95-68, showed paradoxical growth in vivo with significantly higher CFU recovered from mice given CAS at 20 mg/kg than those given CAS at 5 mg/kg, but the effect was not reproducible in a subsequent experiment. When CAS was given prophylactically and therapeutically, improved efficacy and cure rate were observed. Overall, these data indicate that CAS is highly efficacious against systemic murine candidiasis and a paradoxical effect was not reproducibly demonstrated in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Abruzzo, G. K., A. M. Flattery, C. J. Gill, L. Kong, J. G. Smith, V. B. Pikounis, J. M. Balkovec, A. F. Bouffard, J. F. Dropinski, H. Rosen, H. Kropp, and K. Bartizal. 1997. Evaluation of the echinocandin antifungal MK-0991 (L-743,872): efficacies in mouse models of disseminated aspergillosis, candidiasis, and cryptococcosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:2333-2338. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abruzzo, G. K., C. J. Gill, A. M. Flattery, L. Kong, C. Leighton, J. G. Smith, V. B. Pikounis, K. Bartizal, and H. Rosen. 2000. Efficacy of the echinocandin caspofungin against disseminated aspergillosis and candidiasis in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:2310-2318. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clemons, K. V., and D. A. Stevens. 2001. Efficacy of the partricin derivative SPA-S-753 against systemic murine candidosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 47:183-186. - PubMed
-
- Deresinski, S. C., and D. A. Stevens. 2003. Caspofungin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 36:1445-1457. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

