Impact of Enterococcus faecalis on the bactericidal activities of arbekacin, daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a mixed-pathogen pharmacodynamic model
- PMID: 16569844
- PMCID: PMC1426965
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1298-1303.2006
Impact of Enterococcus faecalis on the bactericidal activities of arbekacin, daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a mixed-pathogen pharmacodynamic model
Abstract
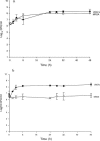
We inoculated an in vitro pharmacodynamic model simultaneously with clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and an enterocin-producing enterococcus (vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis, ampicillin susceptible) at 7 log10 CFU/ml to examine enterocin effects and antimicrobial activity on staphylococci. The investigated antimicrobial regimens were 100 mg arbekacin every 12 h (q12h), 6 mg daptomycin per kg of body weight/day, 600 mg linezolid q12h, and 100 mg tigecycline q24h alone and in combination (daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline) with arbekacin. Simulations were performed in triplicate; bacterial quantification occurred over 48 h, and development of resistance was evaluated throughout. When we evaluated the impact of antimicrobial activity against S. aureus alone, daptomycin demonstrated bactericidal activity (>or=3 log10 CFU/ml kill), whereas arbekacin, linezolid, and tigecycline displayed bacteriostatic activities (<3 log10 CFU/ml kill). In the mixed-pathogen model, early and distinctive stunting of S. aureus growth was noted (1.5 log CFU/ml difference) in the presence of enterocin-producing E. faecalis compared to growth controls run individually (P=0.02). Most noteworthy was that in the presence of enterocin-producing E. faecalis, bactericidal activity was observed with arbekacin and tigecycline and with the addition of arbekacin to linezolid. Antagonism was noted for the combination of tigecycline and arbekacin against S. aureus in the presence of enterocin-producing E. faecalis. Our research demonstrates that the inhibitory effect of E. faecalis contributed significantly to its overall antimicrobial impact on S. aureus. This contribution was enhanced or improved compared to the activity of each antimicrobial alone. Further research is warranted to determine the impact of polymicrobial infections on antimicrobial activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of high-inoculum Staphylococcus aureus on the activities of nafcillin, vancomycin, linezolid, and daptomycin, alone and in combination with gentamicin, in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Dec;48(12):4665-72. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4665-4672.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15561842 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of daptomycin or linezolid in combination with rifampin or gentamicin against biofilm-forming Enterococcus faecalis or E. faecium in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model using simulated endocardial vegetations and an in vivo survival assay using Galleria mellonella larvae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Aug;58(8):4612-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02790-13. Epub 2014 May 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24867993 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of standard- and high-dose daptomycin versus linezolid against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus isolates in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jun;56(6):3174-80. doi: 10.1128/AAC.06439-11. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22470111 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of daptomycin against clinical isolates with reduced susceptibilities to linezolid and quinupristin/dalfopristin.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006 Nov;28(5):385-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2006.07.017. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006. PMID: 17046205 Review.
-
The global prevalence of Daptomycin, Tigecycline, Quinupristin/Dalfopristin, and Linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci strains: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020 Apr 22;9(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13756-020-00714-9. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020. PMID: 32321574 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Eradication of Staphylococcus epidermidis within Biofilms: Comparison of Systemic versus Supratherapeutic Concentrations of Antibiotics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Jun 15;67(6):e0010823. doi: 10.1128/aac.00108-23. Epub 2023 May 8. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37154699 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of arbekacin for high-risk infections in patients with hematological malignancies.Int J Hematol. 2016 Mar;103(3):334-40. doi: 10.1007/s12185-015-1926-6. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Int J Hematol. 2016. PMID: 26715149 Clinical Trial.
-
Minocycline Alone and in Combination with Polymyxin B, Meropenem, and Sulbactam against Carbapenem-Susceptible and -Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an In Vitro Pharmacodynamic Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Feb 17;65(3):e01680-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01680-20. Print 2021 Feb 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33318006 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus strains with various mechanisms of daptomycin resistance developed in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Oct;55(10):4748-54. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00084-11. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21788457 Free PMC article.
-
Polymyxin B Combined with Minocycline: A Potentially Effective Combination against blaOXA-23-harboring CRAB in In Vitro PK/PD Model.Molecules. 2022 Feb 6;27(3):1085. doi: 10.3390/molecules27031085. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cleveland, J., T. J. Montville, I. F. Nes, and M. L. Chikindas. 2001. Bacteriocins: safe, natural antimicrobials for food preservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 71:1-20. - PubMed
-
- Giraffa, G. 2003. Functionality of enterococci in dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 88:215-222. - PubMed
-
- Hanberger, H., L. E. Nilsson, R. Maller, and B. Isaksson. 1991. Pharmacodynamics of daptomycin and vancomycin on Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus demonstrated by studies of initial killing and postantibiotic effect and influence of Ca2+ and albumin on these drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35:1710-1716. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

