Binding of neomycin-class aminoglycoside antibiotics to mutant ribosomes with alterations in the A site of 16S rRNA
- PMID: 16569869
- PMCID: PMC1426975
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1489-1496.2006
Binding of neomycin-class aminoglycoside antibiotics to mutant ribosomes with alterations in the A site of 16S rRNA
Abstract
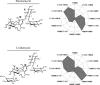
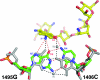
Aminoglycoside antibiotics that bind to the aminoacyl-tRNA site (A site) of the ribosome are composed of a common neamine core in which a glycopyranosyl ring is attached to position 4 of a 2-deoxystreptamine moiety. The core is further substituted by one (ribostamycin), two (neomycin and paromomycin), or three (lividomycin A) additional sugars attached to position 5 of the 2-deoxystreptamine. To study the role of rings III, IV, and V in aminoglycoside binding, we used isogenic Mycobacterium smegmatis DeltarrnB mutants carrying homogeneous populations of mutant ribosomes with alterations in the 16S rRNA A site. MICs were determined to investigate drug-ribosome interactions, and the results were compared with that of the previously published crystal structure of paromomycin bound to the ribosomal A site. Our analysis demonstrates that the stacking interaction between ring I and G1491 is largely sequence independent, that rings III and IV each increase the strength of drug binding to the ribosome, that ring IV of the 6'-NH3+ aminoglycosides compensates for loss of interactions between ring II and U1495 and between ring III and G1491, that the aminoglycosides rely on pseudo-base pairing between ring I and A1408 for binding independently of the number of sugar rings attached to the neamine core, that addition of ring V to the 6'-OH 4,5-aminoglycoside paromomycin does not alter the mode of binding, and that alteration of the U1406.U1495 wobble base pair to the Watson-Crick interaction pair 1406C-1495G yields ribosomal drug susceptibilities to 4,5-aminoglycosides comparable to those seen with the wild-type A site.
Figures



References
-
- Auffinger, P., and E. Westhof. 2001. Water and ion binding around r(UpA)12 and d(TpA)12 oligomers—comparison with RNA and DNA (CpG)12 duplexes. J. Mol. Biol. 305:1057-1072. - PubMed
-
- Carter, A. P., W. M. Clemons, D. E. Brodersen, R. J. Morgan-Warren, B. T. Wimberly, and V. Ramakrishnan. 2000. Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature 407:340-348. - PubMed
-
- Dahlberg, A. E. 1989. The functional role of ribosomal RNA in protein synthesis. Cell 57:525-529. - PubMed
-
- Davies, J., L. Gorini, and B. D. Davis. 1965. Misreading of RNA codewords induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Mol. Pharmacol. 1:93-106. - PubMed
-
- De Stasio, E. A., and A. E. Dahlberg. 1990. Effects of mutagenesis of a conserved base-paired site near the decoding region of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 212:127-133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

