Preclinical evaluation of synthetic -2 RANTES as a candidate vaginal microbicide to target CCR5
- PMID: 16569870
- PMCID: PMC1426989
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1497-1509.2006
Preclinical evaluation of synthetic -2 RANTES as a candidate vaginal microbicide to target CCR5
Abstract
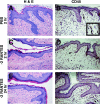
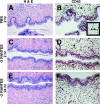
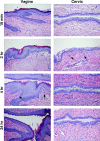
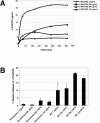
A potential strategy that can be used to combat the worldwide AIDS epidemic is the development of a vaginal microbicide that prevents the sexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Certain CC chemokines, including RANTES, MIP-1alpha, and MIP-1beta, might facilitate the development of such microbicides since they potently suppress HIV-1 infection by binding to CCR5, the viral coreceptor used by most sexually transmitted strains of HIV-1 to enter host cells. In this study, we evaluated whether a CCR5-specific fragment of RANTES that lacks two N-terminal residues (-2 RANTES) and possesses especially potent HIV-1 suppressive activity has toxicity profiles conducive to the advancement of testing in candidate microbicide formulations. Analyses were carried out with a synthetic version of the chemokine, which was formulated with either Novasomes 7474, a nonphospholipid liposome, or methylcellulose gel. Dialysis studies demonstrated that the formulated -2 RANTES was released from both vehicles and retained anti-HIV-1 activity. Preclinical toxicity studies carried out with Swiss Webster mouse and New Zealand White rabbit vaginal irritation models demonstrated minimal inflammation and minimal adverse changes in cervicovaginal tissue integrity after short-term (10 min) and long-term (24 h) exposure to formulations containing up to 1 mg/ml of -2 RANTES. Similarly, no toxicity was observed with formulations of bioactive murine RANTES in the Swiss Webster mouse vaginal irritation model. Overall, these preclinical studies suggest that -2 RANTES is suitable for further testing as a candidate anti-HIV-1 microbicide.
Figures


References
-
- Alkhatib, G., M. Locati, P. E. Kennedy, P. M. Murphy, and E. A. Berger. 1997. HIV-1 coreceptor activity of CCR5 and its inhibition by chemokines: independence from G protein signaling and importance of coreceptor downmodulation. Virology 234:340-348. - PubMed
-
- Reference deleted.
-
- Amara, A., S. L. Gall, O. Schwartz, J. Salamero, M. Montes, P. Loetscher, M. Baggiolini, J. L. Virelizier, and F. Arenzana-Seisdedos. 1997. HIV coreceptor downregulation as antiviral principle: SDF-1alpha-dependent internalization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 contributes to inhibition of HIV replication. J. Exp. Med. 186:139-146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Physiological Society. 1996. Guiding principles in the care and use of animals. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
-
- AVMA Panel on Euthanasia. 2001. 2000 report of the AVMA Panel on Euthanasia. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 218:669-696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

