Cardiac toxicity of trastuzumab in metastatic breast cancer patients previously treated with high-dose chemotherapy: a retrospective study
- PMID: 16570045
- PMCID: PMC2361220
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603060
Cardiac toxicity of trastuzumab in metastatic breast cancer patients previously treated with high-dose chemotherapy: a retrospective study
Abstract
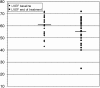
HER-2 overexpression is associated to a poor prognosis in high-risk and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy (HDC). HER-2 status is also a predictive factor and when trastuzumab is administered in combination with or sequentially to chemotherapy, a significant disease-free and/or overall survival improvement has been observed in HER-2+ early and MBC. Unfortunately, in both settings, trastuzumab is associated with an increased risk of cardiac dysfunction (CD). We have reviewed the clinical charts of HER-2-overexpressing MBC patients treated with trastuzumab after HDC. Age, baseline left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), radiation therapy on cardiac area, exposure to anthracycline, single or multiple transplant, high-dose agents, trastuzumab treatment duration were recorded as potential risk factors. In total, 53 patients have been included in the analysis. Median LVEF at baseline was 60.5%; at the end of trastuzumab (data available for 28 patients only), it was 55% (P = 0.01). Five out of the 28 (17.9%) patients experienced CD. Two out of 53 (3.8%) patients developed a congestive heart failure. Age > or = 50 years and multiple transplant procedure were potential risk factors for CD. The overall incidence of CD observed in this population of HER-2+ MBC patients treated with trastuzumab after HDC is not superior to that reported with concomitant trastuzumab and anthracyclines. However, patients with age > or = 50 years or receiving multiple course of HDC should be considered at risk for CD.
Figures
References
-
- Alidina A, Lawrence D, Ford LA, Baer MR, Bambach B, Bernstein SH, Czuzman MS, Slack JL, Spangenthal E, Wetzler M, Barcos MP, Proulx GM, Anderson B, McCarthy Jr PL (1999) Thiotepa-associated cardiomiopathy during blood or marrow transplantation: association with the female sex and cardiac risk factors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 5: 322–327 - PubMed
-
- Bengala C, Danesi R, Guarneri V, Pazzagli I, Donati S, Favre C, Fogli S, Biadi O, Innocenti F, Del Tacca M, Mariani M, Conte PF (2003) High-dose consolidation chemotherapy with idarubicin and alkylating agents following induction with gemcitabine–epirubicin–paclitaxel in metastatic breast cancer: a dose finding study. Bone Marrow Transplant 31: 275–280 - PubMed
-
- Bengala C, Pazzagli I, Innocenti F, Donati S, Favre C, Menconi MC, Greco F, Danesi R, Orlandini C, Guarneri V, Del Tacca M, Conte PF (2001) High-dose thiotepa and melphalan with hempoietic progenitor support following induction therapy with epirubicin–paclitaxel–containing regimens in metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Ann Oncol 12: 69–74 - PubMed
-
- Bergh J, Wiklund T, Erikstein B, Lidbrink E, Lindman H, Malmstrom P, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P, Bengtsson NO, Soderlund G, Anker G, Wist E, Ottosson S, Salminen E, Ljungman P, Holte H, Nilsson J, Blomqvist C, Wilking N (2000) Tailored fluorouracil, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide compared with marrow-supported high-dose chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment for high-risk breast cancer: a randomized trial of Scandinavian Breast Group 9401 study. Lancet 356: 1384–1391 - PubMed
-
- Bitran JD, Samuels B, Trujillo Y, Klein L, Schroeder L, Martinec J (1996) Her2/neu overxpression is associated with treatment failure in women with high-risk stage II and stage IIIA breast cancer (>10 involved lymph nodes) treated with high-dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic progenitor cell support following standard-dose adjuvant chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2: 1509–1513 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous