Phase II study of erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
- PMID: 16570047
- PMCID: PMC2361254
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603055
Phase II study of erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
Abstract
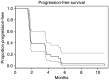
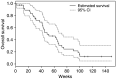
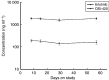
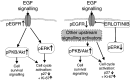
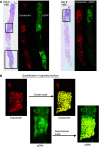
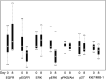
Erlotinib (Tarceva, OSI-774), a potent epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR), was evaluated in a phase II study to assess its activity in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. In all, 38 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer were treated with erlotinib at a continuous daily oral dose of 150 mg. Radiological evaluation was carried out every 8 weeks and tumour biopsies were performed before treatment and on day 8. Of 31 evaluable patients, 19 (61%) had progressive disease and 12 (39%) had stable disease (s.d.). The median time to progression for those patients having s.d. was 123 days (range 108-329 days). The most common adverse events were rash in 34 patients and diarrhoea in 23 patients. Correlative studies were conducted to investigate the effect of erlotinib on downstream signalling. Tumour tissue correlations were based on usable tissue from eight match paired tumour samples pre- and on therapy, and showed a statistically significant decrease in the median intensity of both pEGFR (P=0.008) and phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) (P=0.008) a week after commencement of treatment. No other statistically significant change in tumour markers was observed. Erlotinib was well tolerated with the most common toxicities being rash and diarrhoea. More than one-third of evaluable patients had s.d. for a minimum of 8 weeks. Correlative studies showed a reduction in phosphorylated EGFR and ERK in tumour tissue post-treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erlotinib: CP 358774, NSC 718781, OSI 774, R 1415.Drugs R D. 2003;4(4):243-8. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304040-00006. Drugs R D. 2003. PMID: 12848590
-
Phase II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy combined with erlotinib for patients with limited but progressive metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Dec 1;32(34):3824-30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.7412. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25349291 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I dose-escalation study of oral vinflunine in combination with erlotinib in pre-treated and unselected EGFR patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;73(2):231-6. doi: 10.1007/s00280-013-2342-3. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24220936 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Erlotinib: a new therapeutic approach for non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2003 Aug;12(8):1395-401. doi: 10.1517/13543784.12.8.1395. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12882624 Review.
-
Erlotinib in non-small-cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007 Oct;8(15):2579-92. doi: 10.1517/14656566.8.15.2579. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17931092 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of personalized medicine in metastatic colorectal cancer: an evolving landscape.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2013 Sep;6(5):381-95. doi: 10.1177/1756283X13491797. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24003339 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy in rectal cancer.Oncology (Williston Park). 2007 Aug;21(9):1055-65; discussion 1065, 1070, 1075 passim. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007. PMID: 17910311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase I trial of oxaliplatin, infusional 5-fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX4) with erlotinib and bevacizumab in colorectal cancer.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2010 Dec;9(5):297-304. doi: 10.3816/CCC.2010.n.043. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21208844 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antitumor activity of the HER2 dimerization inhibitor pertuzumab on human colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009 Oct;135(10):1377-86. doi: 10.1007/s00432-009-0579-3. Epub 2009 Apr 2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19340455 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of signal transduction pathways in colorectal cancer: implications for therapeutic resistance.PeerJ. 2021 Oct 22;9:e12338. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12338. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34733591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpenter G, Cohen S (1990) Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 265: 7709–7712 - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, Chau I, Van Cutsem E (2004) Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351: 337–345 - PubMed
-
- Fisher GA, Kuo T, Cho CD, Halsey J, Jambalos CN, Schwartz EJ, Robert RV, Advani RH, Wakelee HA, Sikic BI (2004) A phase II study of gefitinib in combination with FOLFOX-4 (IFOX) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22: 14S (abstr. 187)
-
- Giacchetti S, Perpoint B, Zidani R, Le Bail N, Faggiuolo R, Focan C, Chollet P, Llory JF, Letourneau Y, Coudert B, Bertheaut-Cvitkovic F, Larregain-Fournier D, Le Rol A, Walter S, Adam R, Misset JL, Levi F (2000) Phase III multicenter randomized trial of oxaliplatin added to chronomodulated fluorouracil–leucovorin as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18: 136–147 - PubMed
-
- Gordon AN, Finkler N, Edwards RP, Garcia AA, Crozier M, Irwin DH, Barrett E (2005) Phase 2 evaluation of OSI-774, a potent oral antagonist of the EGFR-TK in patients with advanced ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 15: 785–792 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

