Systemic inflammatory response in erderly patients following hernioplastical operation
- PMID: 16571118
- PMCID: PMC1475883
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4933-3-3
Systemic inflammatory response in erderly patients following hernioplastical operation
Abstract
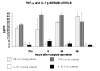
The number of old and oldest old patients undergoing surgery of varying severity is increasing. Ageing is a process that changes the performances of most physiological systems and increases susceptibility to diseases and death; accordingly, host responses to surgical stress are altered with ageing and the occurrence of age-related increase in susceptibility to post-operative complications has been claimed. Twenty-four male patients undergoing Lichtenstein (LH) hernioplasty for unilateral inguinal hernia were included in this study and divided in two groups (Young and Old respectively), according to their age. As expression of the acute phase response, we measured changes in concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and Interleukin-1beta, leukocytes, acute phase proteins C-reactive protein and alpha 1-antitrypsin. Elderly humans showed prolonged and strong inflammatory activity compared to younger subjects in response to surgical stress, indicating that the acute-phase response to surgical stress of elderly humans varies from that of the young, showing initial hyperactivity and a delayed termination of the response. Thus, the acute phase response to surgical stress is higher in old subjects, but the clinical significance of this remains unclear. It is not known whether a causal relationship exists between this stronger acute phase response and the increases in susceptibility to post-operative complications observed in aged patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Augmented enhancement of in vitro production of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients undergoing simultaneous resection of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.Crit Care Med. 1999 May;27(5):929-36. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199905000-00028. Crit Care Med. 1999. PMID: 10362415
-
The inflammatory response to open tension-free inguinal hernioplasty versus conventional repairs.Am J Surg. 1998 Mar;175(3):179-82. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(97)00293-6. Am J Surg. 1998. PMID: 9560115
-
[Cytokines and soluble cytokine receptors in the perioperative period].Sb Lek. 2002;103(2):273-82. Sb Lek. 2002. PMID: 12688152 Czech.
-
Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002;8:6-48. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12690937 Review.
-
[Similarity and synergy of trauma and sepsis: role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6].Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 1996 Sep;34(3):141-9. Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 1996. PMID: 9084538 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Systemic inflammatory response after hernia repair: a systematic review.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017 Nov;402(7):1023-1037. doi: 10.1007/s00423-017-1618-1. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017. PMID: 28831565
-
Plasma proteinase inhibitory activity in ectopic and molar pregnancy.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2008 Oct;23(4):352-5. doi: 10.1007/s12291-008-0077-4. Epub 2008 Dec 20. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2008. PMID: 23105785 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological reaction and oxidative stress after light or heavy polypropylene mesh implantation in inguinal hernioplasty: A CONSORT-prospective, randomized, clinical trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jun;95(24):e3791. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003791. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27310955 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Proinflammatory cytokines in Egyptian elderly with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Lung India. 2010 Oct;27(4):225-9. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.71956. Lung India. 2010. PMID: 21139720 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in stress response between patients undergoing transurethral resection versus endoscopic laser ablation of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia.Lasers Med Sci. 2008 Jan;23(1):65-70. doi: 10.1007/s10103-007-0462-x. Epub 2007 Apr 28. Lasers Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 17468896
References
-
- Vasto S, Caruso C. Immunity & Ageing: a new journal looking at ageing from an immunological point of view. Immun Ageing. 2004;1:1. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-1-1. http://www.immunityageing.com/content/1/1/1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

