"Per cell" normalization method for mRNA measurement by quantitative PCR and microarrays
- PMID: 16571132
- PMCID: PMC1448209
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-64
"Per cell" normalization method for mRNA measurement by quantitative PCR and microarrays
Abstract
Background: Transcriptome data from quantitative PCR (Q-PCR) and DNA microarrays are typically obtained from a fixed amount of RNA collected per sample. Therefore, variations in tissue cellularity and RNA yield across samples in an experimental series compromise accurate determination of the absolute level of each mRNA species per cell in any sample. Since mRNAs are copied from genomic DNA, the simplest way to express mRNA level would be as copy number per template DNA, or more practically, as copy number per cell.
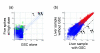
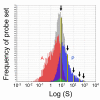
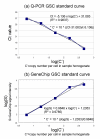
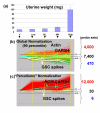
Results: Here we report a method (designated the "Percellome" method) for normalizing the expression of mRNA values in biological samples. It provides a "per cell" readout in mRNA copy number and is applicable to both quantitative PCR (Q-PCR) and DNA microarray studies. The genomic DNA content of each sample homogenate was measured from a small aliquot to derive the number of cells in the sample. A cocktail of five external spike RNAs admixed in a dose-graded manner (dose-graded spike cocktail; GSC) was prepared and added to each homogenate in proportion to its DNA content. In this way, the spike mRNAs represented absolute copy numbers per cell in the sample. The signals from the five spike mRNAs were used as a dose-response standard curve for each sample, enabling us to convert all the signals measured to copy numbers per cell in an expression profile-independent manner. A series of samples was measured by Q-PCR and Affymetrix GeneChip microarrays using this Percellome method, and the results showed up to 90 % concordance.
Conclusion: Percellome data can be compared directly among samples and among different studies, and between different platforms, without further normalization. Therefore, "percellome" normalization can serve as a standard method for exchanging and comparing data across different platforms and among different laboratories.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Large scale real-time PCR validation on gene expression measurements from two commercial long-oligonucleotide microarrays.BMC Genomics. 2006 Mar 21;7:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-59. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16551369 Free PMC article.
-
An alternative method to amplify RNA without loss of signal conservation for expression analysis with a proteinase DNA microarray in the ArrayTube format.BMC Genomics. 2006 Jun 12;7:144. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-144. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16768788 Free PMC article.
-
Normalization of low-density microarray using external spike-in controls: analysis of macrophage cell lines expression profile.BMC Genomics. 2007 Jan 17;8:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-17. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17229315 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic DNA as a general cohybridization standard for ratiometric microarrays.Methods Enzymol. 2006;410:237-79. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)10012-9. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 16938555 Review.
-
Standards in gene expression microarray experiments.Methods Enzymol. 2006;411:63-78. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)11005-8. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 16939786 Review.
Cited by
-
Whole-body scanning PCR; a highly sensitive method to study the biodistribution of mRNAs, noncoding RNAs and therapeutic oligonucleotides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(15):e145. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt515. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23766292 Free PMC article.
-
Minichromosome maintenance 2 bound with retroviral Gp70 is localized to cytoplasm and enhances DNA-damage-induced apoptosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40129. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040129. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768239 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lncRNA BDNF-AS inhibited the progression of multiple myeloma by targeting the miR-125a/b-5p-BCL2 axis.Immun Ageing. 2022 Jan 3;19(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12979-021-00258-5. Immun Ageing. 2022. PMID: 34980181 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive pattern of let-7 family microRNAs in aggressive carcinoma of the oral tongue in young patients.Oncol Lett. 2016 Sep;12(3):1729-1736. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4892. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27602107 Free PMC article.
-
NANOS2 interacts with the CCR4-NOT deadenylation complex and leads to suppression of specific RNAs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3594-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908664107. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133598 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

