Spike-frequency adaptation and intrinsic properties of an identified, looming-sensitive neuron
- PMID: 16571737
- PMCID: PMC1995006
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00075.2006
Spike-frequency adaptation and intrinsic properties of an identified, looming-sensitive neuron
Abstract
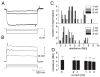
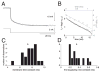
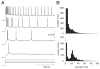
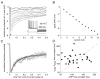
We investigated in vivo the characteristics of spike-frequency adaptation and the intrinsic membrane properties of an identified, looming-sensitive interneuron of the locust optic lobe, the lobula giant movement detector (LGMD). The LGMD had an input resistance of 4-5 MOmega, a membrane time constant of about 8 ms, and exhibited inward rectification and rebound spiking after hyperpolarizing current pulses. Responses to depolarizing current pulses revealed the neuron's intrinsic bursting properties and pronounced spike-frequency adaptation. The characteristics of adaptation, including its time course, the attenuation of the firing rate, the mutual dependency of these two variables, and their dependency on injected current, closely followed the predictions of a model first proposed to describe the adaptation of cat visual cortex pyramidal neurons in vivo. Our results thus validate the model in an entirely different context and suggest that it might be applicable to a wide variety of neurons across species. Spike-frequency adaptation is likely to play an important role in tuning the LGMD and in shaping the variability of its responses to visual looming stimuli.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Spike frequency adaptation mediates looming stimulus selectivity in a collision-detecting neuron.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Mar;12(3):318-26. doi: 10.1038/nn.2259. Epub 2009 Feb 8. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19198607 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping the collision selectivity in a looming sensitive neuron model with parallel ON and OFF pathways and spike frequency adaptation.Neural Netw. 2018 Oct;106:127-143. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Neural Netw. 2018. PMID: 30059829
-
Role of spike-frequency adaptation in shaping neuronal response to dynamic stimuli.Biol Cybern. 2009 Jun;100(6):505-20. doi: 10.1007/s00422-009-0304-y. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Biol Cybern. 2009. PMID: 19381681 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial distribution of inputs and local receptive field properties of a wide-field, looming sensitive neuron.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Apr;93(4):2240-53. doi: 10.1152/jn.00965.2004. Epub 2004 Nov 17. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15548622
-
Responses of a looming-sensitive neuron to compound and paired object approaches.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Mar;95(3):1428-41. doi: 10.1152/jn.01037.2005. Epub 2005 Nov 30. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16319198
Cited by
-
Impact of neural noise on a sensory-motor pathway signaling impending collision.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Feb;107(4):1067-79. doi: 10.1152/jn.00607.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 23. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22114160 Free PMC article.
-
Feedforward Inhibition Conveys Time-Varying Stimulus Information in a Collision Detection Circuit.Curr Biol. 2018 May 21;28(10):1509-1521.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 May 10. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29754904 Free PMC article.
-
Negative autoregulation linearizes the dose-response and suppresses the heterogeneity of gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 31;106(13):5123-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809901106. Epub 2009 Mar 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19279212 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinspired figure-ground discrimination via visual motion smoothing.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Apr 21;19(4):e1011077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011077. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37083880 Free PMC article.
-
Spike frequency adaptation mediates looming stimulus selectivity in a collision-detecting neuron.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Mar;12(3):318-26. doi: 10.1038/nn.2259. Epub 2009 Feb 8. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19198607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed B, Anderson JC, Douglas RJ, Martin KAC, Whitteridge D. Estimates of the net excitatory currents evoked by visual stimulation of identified neurons in cat visual cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1998;8:462–476. - PubMed
-
- Benda J, Herz AVM. A universal model for spike-frequency adaptation. Neural Comput. 2003;15:2523–2564. - PubMed
-
- Borg-Gaham L, Monier C, Fregnac Y. Voltage-clamp measurement of visually-evoked conductances with whole-cell patch recordings in primary visual cortex. J Physiol (Paris) 1996;90:185–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

