CD8+ lymphocyte-mediated injury of dorsal root ganglion neurons during lentivirus infection: CD154-dependent cell contact neurotoxicity
- PMID: 16571746
- PMCID: PMC6673847
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4767-05.2006
CD8+ lymphocyte-mediated injury of dorsal root ganglion neurons during lentivirus infection: CD154-dependent cell contact neurotoxicity
Abstract
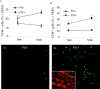
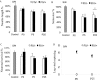
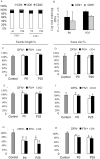
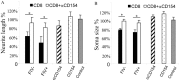
Neuronal damage in dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) with accompanying axonal injury is a key feature of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related distal sensory polyneuropathy (DSP). In a model of HIV-related DSP, we observed numerous CD3+ T lymphocytes (p < 0.05) in DRGs from feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV)-infected animals, which also exhibited low CD4+ and high CD8+ lymphocyte levels in blood accompanied by a selective loss of small-diameter sural nerve axons (p < 0.05). FIV-infected lymphocytes cocultured with syngeneic DRGs caused neuronal damage, indicated by neurite retraction, neuronal soma atrophy, and loss (p < 0.05). In contrast, supernatants from FIV-infected or uninfected lymphocytes were minimally neurotoxic, despite high FIV virion levels. Among lymphocyte subsets cocultured with DRG cultures, CD8+ T cells from both FIV-infected and uninfected lymphocytes selectively caused DRG neuronal injury (p < 0.05). FIV-infected CD8+ T cells showed markedly increased CD154 expression (p < 0.05), whereas neurons were the predominant cells expressing CD40 in DRGs. Blocking CD154 on activated CD8+ T cells protected DRG neurons (p < 0.05). These findings indicated that CD8+ T cells were principal effectors of DRG neuronal injury after FIV infection through a CD40-CD154 interaction in a cell contact-dependent manner.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lentivirus infection causes neuroinflammation and neuronal injury in dorsal root ganglia: pathogenic effects of STAT-1 and inducible nitric oxide synthase.J Immunol. 2005 Jul 15;175(2):1118-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.2.1118. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16002713
-
Impaired T-cell priming and proliferation in cats infected with feline immunodeficiency virus.AIDS. 1992 Mar;6(3):287-93. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199203000-00005. AIDS. 1992. PMID: 1348945
-
Didanosine causes sensory neuropathy in an HIV/AIDS animal model: impaired mitochondrial and neurotrophic factor gene expression.Brain. 2007 Aug;130(Pt 8):2011-23. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm148. Epub 2007 Jul 6. Brain. 2007. PMID: 17616550
-
Selective thymocyte depletion and immunoglobulin coating in the thymus of cats infected with feline immunodeficiency virus.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1997 May 1;13(7):611-20. doi: 10.1089/aid.1997.13.611. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1997. PMID: 9135879
-
Early events in the immunopathogenesis of feline retrovirus infections.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1991 Nov 15;199(10):1311-5. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1991. PMID: 1666073 Review.
Cited by
-
T cells at the interface of neuroimmune communication.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Apr;153(4):894-903. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.10.026. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37952833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of HIV peripheral neuropathy.Future Virol. 2014 May 1;9(5):465-474. doi: 10.2217/fvl.14.28. Future Virol. 2014. PMID: 25214880 Free PMC article.
-
Skin Resident T Cell Interactions with NPY1R+ Neurons During Wound Repair Are Impaired by Obesity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 9:2025.06.06.658336. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.06.658336. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40661589 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Peripheral role of cathepsin S in Th1 cell-dependent transition of nerve injury-induced acute pain to a chronic pain state.J Neurosci. 2014 Feb 19;34(8):3013-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3681-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24553941 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinase-activated receptor-1 mediates dorsal root ganglion neuronal degeneration in HIV/AIDS.Brain. 2011 Nov;134(Pt 11):3209-21. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr242. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Brain. 2011. PMID: 22021895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abendroth A, Simmons A, Efstathiou S, Pereira RA (2000). Infection with an H2 recombinant herpes simplex virus vector results in expression of MHC class I antigens on the surfaces of human neuroblastoma cells in vitro and mouse sensory neurons in vivo. J Gen Virol 81:2375–2383. - PubMed
-
- Araujo AP, Nascimento OJ, Garcia OS (2000). Distal sensory polyneuropathy in a cohort of HIV-infected children over five years of age. Pediatrics 106:E35. - PubMed
-
- Bien CG, Bauer J, Deckwerth TL, Wiendl H, Deckert M, Wiestler OD, Schramm J, Elger CE, Lassmann H (2002). Destruction of neurons by cytotoxic T cells: a new pathogenic mechanism in Rasmussen's encephalitis. Ann Neurol 51:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Boche D, Khatissian E, Gray F, Falanga P, Montagnier L, Hurtrel B (1999). Viral load and neuropathology in the SIV model. J Neurovirol 5:232–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
