Rostral elements of sympatho-motor circuitry: a virally mediated transsynaptic tracing study
- PMID: 16571749
- PMCID: PMC6673864
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5283-05.2006
Rostral elements of sympatho-motor circuitry: a virally mediated transsynaptic tracing study
Abstract
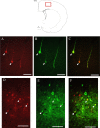
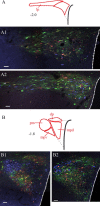
Numerous physiological and emotionally motivated behaviors, including locomotion, exercise, escape, and attack behaviors as well as passive coping responses, require concomitant activation of motor and sympathetic efferents. Such functional heterogeneity suggests the existence of dual function neurons that can simultaneously coordinate motor and sympathetic output. Because previous physiological investigations have implicated a number of mesencephalic and telencephalic regions in mediating these behaviors, we hypothesized the presence of dual function sympatho-motor neurons in these neural structures. To test this hypothesis, we used recombinant strains of the pseudorabies virus (PRV) for transsynaptic tract-tracing. PRV-152, a strain that expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein, was injected into sympathectomized gastrocnemius muscle, whereas PRV-BaBlu, which expresses beta-galactosidase, was injected into the adrenal gland in the same animals. Although coinfected neurons were detected in a number of mesencephalic and telencephalic regions, >50% of such neurons were located within specific subdivisions of two general areas: the hypothalamus and periaqueductal gray. These subdivisions included the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray, dorsomedial hypothalamus, dorsolateral lateral hypothalamus, and ventral portion of the medial parvocellular subdivision of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN). A subset of the sympatho-motor neurons within the PVN also contained either arginine vasopressin or oxytocin. This sympatho-motor circuitry likely plays an important role in mediating different aspects of stress responses and emotionally motivated behaviors.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Relationship of presympathetic-premotor neurons to the serotonergic transmitter system in the rat brainstem.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Dec 20;499(6):882-96. doi: 10.1002/cne.21129. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 17072838
-
Brainstem substrates of sympatho-motor circuitry identified using trans-synaptic tracing with pseudorabies virus recombinants.J Neurosci. 2003 Jun 1;23(11):4657-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-11-04657.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12805305 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct populations of presympathetic-premotor neurons express orexin or melanin-concentrating hormone in the rat lateral hypothalamus.J Comp Neurol. 2007 Dec 10;505(5):586-601. doi: 10.1002/cne.21511. J Comp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17924541
-
Organization of brain somatomotor-sympathetic circuits.Exp Brain Res. 2008 May;187(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s00221-008-1337-5. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Exp Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18369609 Review.
-
New developments in tracing neural circuits with herpesviruses.Virus Res. 2005 Aug;111(2):235-49. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.012. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 15893400 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Functions of Hypothalamic Oxytocin and its Regulation.ASN Neuro. 2022 Jan-Dec;14:17590914221100706. doi: 10.1177/17590914221100706. ASN Neuro. 2022. PMID: 35593066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central stress-integrative circuits: forebrain glutamatergic and GABAergic projections to the dorsomedial hypothalamus, medial preoptic area, and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.Brain Struct Funct. 2014 Jul;219(4):1287-303. doi: 10.1007/s00429-013-0566-y. Epub 2013 May 10. Brain Struct Funct. 2014. PMID: 23661182 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the Brain-Wide Cholinergic Neurons Projecting to Skeletal Muscle in Mice by High-Throughput Light Sheet Tomography.Neurosci Bull. 2021 Feb;37(2):267-270. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00552-0. Epub 2020 Jul 26. Neurosci Bull. 2021. PMID: 32715391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hypothalamic-autonomic control of energy homeostasis.Endocrine. 2015 Nov;50(2):276-91. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0658-y. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Endocrine. 2015. PMID: 26089260 Review.
-
Rapid-onset hypoglycemia suppresses Fos expression in discrete parts of the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):R1177-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00042.2016. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27030665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahamson EE, Moore RY (2001). The posterior hypothalamic area: chemoarchitecture and afferent connections. Brain Res 889:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Agelink MW, Majewski T, Wurthmann C, Postert T, Linka T, Rotterdam S, Klieser E (2001). Autonomic neurocardiac function in patients with major depression and effects of antidepressive treatment with nefazodone. J Affect Disord 62:187–198. - PubMed
-
- Allen GV, Cechetto DF (1992). Functional and anatomical organization of cardiovascular pressor and depressor sites in the lateral hypothalamic area: I. Descending projections. J Comp Neurol 315:313–332. - PubMed
-
- Bandler R (1982). Induction of ‘rage' following microinjections of glutamate into midbrain but not hypothalamus of cats. Neurosci Lett 30:183–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
