Role of residues 121 to 124 of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in virus assembly and virus-host interaction
- PMID: 16571787
- PMCID: PMC1440435
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.3701-3711.2006
Role of residues 121 to 124 of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in virus assembly and virus-host interaction
Abstract
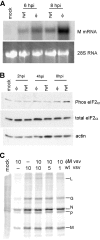
The recent solution of the crystal structure of a fragment of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix (M) protein suggested that amino acids 121 to 124, located on a solvent-exposed loop of the protein, are important for M protein self-association and association with membranes. These residues were mutated from the hydrophobic AVLA sequence to the polar sequence DKQQ. Expression and purification of this mutant from bacteria showed that it was structurally stable and that the mutant M protein had self-association kinetics similar to those of the wild-type M protein. Analysis of the membrane association of M protein in the context of infection with isogenic recombinant viruses showed that both wild-type and mutant M proteins associated with membranes to the same extent. Virus expressing the mutant M protein did show an approximately threefold-lower binding affinity of M protein for nucleocapsid-M complexes. In contrast to the relatively minor effects of the M protein mutation on virus assembly, the mutant virus exhibited growth restriction in MDBK but not BHK cells, a slower induction of apoptosis, and lower viral-protein synthesis. Despite translating less viral protein, the mutant virus produced more viral mRNA, showing that the mutant virus could not effectively promote viral translation. These results demonstrate that the 121-to-124 region of the VSV M protein plays a minor role in virus assembly but is involved in virus-host interactions and VSV replication by augmenting viral-mRNA translation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Matrix protein and another viral component contribute to induction of apoptosis in cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus.J Virol. 2001 Dec;75(24):12169-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.24.12169-12181.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11711608 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA and inhibition of translation of cellular mRNA--is there a P function in vesicular stomatitis virus?J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):504-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.38.2.504-517.1981. J Virol. 1981. PMID: 6264124 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of vesicular stomatitis virus M protein mutants in cell rounding is correlated with the ability to inhibit host gene expression and is not correlated with virus assembly function.Virology. 1997 Mar 3;229(1):77-89. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.8415. Virology. 1997. PMID: 9123880
-
Identification of two additional translation products from the matrix (M) gene that contribute to vesicular stomatitis virus cytopathology.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(16):8011-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.8011-8018.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12134006 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly functions of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein are not disrupted by mutations at major sites of phosphorylation.Virology. 1995 Feb 1;206(2):894-903. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1012. Virology. 1995. PMID: 7856102
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM model of the bullet-shaped vesicular stomatitis virus.Science. 2010 Feb 5;327(5966):689-93. doi: 10.1126/science.1181766. Science. 2010. PMID: 20133572 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein mutations that affect association with host membranes and viral nucleocapsids.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 13;284(7):4500-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808136200. Epub 2008 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19088071 Free PMC article.
-
The family Rhabdoviridae: mono- and bipartite negative-sense RNA viruses with diverse genome organization and common evolutionary origins.Virus Res. 2017 Jan 2;227:158-170. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27773769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complexes of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein with host Rae1 and Nup98 involved in inhibition of host transcription.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002929. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002929. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23028327 Free PMC article.
-
The Deoptimization of Rabies Virus Matrix Protein Impacts Viral Transcription and Replication.Viruses. 2019 Dec 18;12(1):4. doi: 10.3390/v12010004. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31861477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed, M., M. O. McKenzie, S. Puckett, M. Hojnacki, L. Poliquin, and D. S. Lyles. 2003. Ability of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus to suppress beta interferon gene expression is genetically correlated with the inhibition of host RNA and protein synthesis. J. Virol. 77:4646-4657. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Connor, J. H., and D. S. Lyles. 2005. Inhibition of host and viral translation during vesicular stomatitis virus infection. eIF2 is responsible for the inhibition of viral but not host translation. J. Biol. Chem. 280:13512-13519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

