Systemic immunization with an ALVAC-HIV-1/protein boost vaccine strategy protects rhesus macaques from CD4+ T-cell loss and reduces both systemic and mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus SHIVKU2 RNA levels
- PMID: 16571790
- PMCID: PMC1440474
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.3732-3742.2006
Systemic immunization with an ALVAC-HIV-1/protein boost vaccine strategy protects rhesus macaques from CD4+ T-cell loss and reduces both systemic and mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus SHIVKU2 RNA levels
Abstract
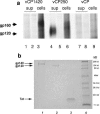
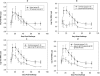
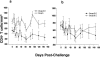
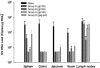
Transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) occurs primarily via the mucosal route, suggesting that HIV-1 vaccines may need to elicit mucosal immune responses. Here, we investigated the immunogenicity and relative efficacy of systemic immunization with two human ALVAC-HIV-1 recombinant vaccines expressing Gag, Pol, and gp120 (vCP250) or Gag, Pol, and gp160 (vCP1420) in a prime-boost protocol with their homologous vaccine native Env proteins. The relative efficacy was measured against a high-dose mucosal exposure to the pathogenic neutralization-resistant variant SHIV(KU2) (simian-human immunodeficiency virus). Systemic immunization with both vaccine regimens decreased viral load levels not only in blood but unexpectedly also in mucosal sites and protected macaques from peripheral CD4+ T-cell loss. This protective effect was stronger when the gp120 antigen was included in the vaccine. Inclusion of recombinant Tat protein in the boosting phase along with the Env protein did not contribute further to the preservation of CD4+ T cells. Thus, systemic immunization with ALVAC-HIV-1 vaccine candidates elicits anti-HIV-1 immune responses able to contain virus replication also at mucosal sites in macaques.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vaccination of rhesus macaques with recombinant Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin Env V3 elicits neutralizing antibody-mediated protection against simian-human immunodeficiency virus with a homologous but not a heterologous V3 motif.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1452-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1452-1462.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650171 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization of rhesus macaques with a polyvalent DNA prime/protein boost human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vaccine elicits protective antibody response against simian human immunodeficiency virus of R5 phenotype.Virology. 2006 May 10;348(2):341-53. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.12.029. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16460776
-
Oral Immunization with Recombinant Vaccinia Virus Prime and Intramuscular Protein Boost Provides Protection against Intrarectal Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Challenge in Macaques.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Dec 30;23(3):204-12. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00597-15. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26718849 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal immunity and HIV-1 infection: applications for mucosal AIDS vaccine development.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;354:157-79. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_119. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21203884 Review.
-
Antibody-mediated immune exclusion of HIV.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017 May;12(3):222-228. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000369. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28422786 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced protection from simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251 infection afforded by memory CD8+ T cells induced by vaccination during CD4+ T-cell deficiency.J Virol. 2008 Oct;82(19):9629-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00893-08. Epub 2008 Jul 30. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18667509 Free PMC article.
-
Prime-boost vaccination with a combination of proteosome-degradable and wild-type forms of two influenza proteins leads to augmented CTL response.Vaccine. 2008 Apr 24;26(18):2177-85. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.02.050. Epub 2008 Mar 14. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18400345 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of poxvirus vaccines.Viruses. 2015 Apr 7;7(4):1726-803. doi: 10.3390/v7041726. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25853483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monkeying around with HIV vaccines: using rhesus macaques to define 'gatekeepers' for clinical trials.Nat Rev Immunol. 2009 Oct;9(10):717-28. doi: 10.1038/nri2636. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19859066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of IL-7 and IL-15 signaling affects interferon-γ production by, more than survival of, small intestinal intraepithelial memory CD8+ T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Dec;41(12):3513-28. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141453. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21928282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abimiku, A. G., G. Franchini, J. Tartaglia, K. Aldrich, M. Myagkikh, P. D. Markham, P. Chong, M. Klein, M. P. Kieny, E. Paoletti, R. C. Gallo, and M. Robert-Guroff. 1995. HIV-1 recombinant poxvirus vaccine induces cross-protection against HIV-2 challenge in rhesus macaques. Nat. Med. 1:321-329. - PubMed
-
- Amara, R. R., F. Villinger, J. D. Altman, S. L. Lydy, S. P. O'Neil, S. I. Staprans, D. C. Montefiori, Y. Xu, J. G. Herndon, L. S. Wyatt, M. A. Candido, N. L. Kozyr, P. L. Earl, J. M. Smith, H. L. Ma, B. D. Grimm, M. L. Hulsey, J. Miller, H. M. McClure, J. M. McNicholl, B. Moss, and H. L. Robinson. 2001. Control of a mucosal challenge and prevention of AIDS by a multiprotein DNA/MVA vaccine. Science 292:69-74. - PubMed
-
- Andersson, S., B. Makitalo, R. Thorstensson, G. Franchini, J. Tartaglia, K. Limbach, E. Paoletti, P. Putkonen, and G. Biberfeld. 1996. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a human immunodeficiency virus type 2 recombinant canarypox (ALVAC) vaccine candidate in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Infect. Dis. 174:977-985. - PubMed
-
- Barouch, D. H., A. Craiu, M. J. Kuroda, J. E. Schmitz, X. X. Zheng, S. Santra, J. D. Frost, G. R. Krivulka, M. A. Lifton, C. L. Crabbs, G. Heidecker, H. C. Perry, M. E. Davies, H. Xie, C. E. Nickerson, T. D. Steenbeke, C. I. Lord, D. C. Montefiori, T. B. Strom, J. W. Shiver, M. G. Lewis, and N. L. Letvin. 2000. Augmentation of immune responses to HIV-1 and simian immunodeficiency virus DNA vaccines by IL-2/Ig plasmid administration in rhesus monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:4192-4197. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belshe, R., G. Franchini, M. P. Girard, F. Gotch, P. Kaleebu, M. L. Marthas, M. B. McChesney, R. McCullough, F. Mhalu, D. Salmon-Ceron, R. P. Sekaly, K. van Rompay, B. Verrier, B. Wahren, and M. Weissenbacher. 2004. Support for the RV144 HIV vaccine trial. Science 305:177-180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

