Intrarectal immunization with rotavirus 2/6 virus-like particles induces an antirotavirus immune response localized in the intestinal mucosa and protects against rotavirus infection in mice
- PMID: 16571799
- PMCID: PMC1440434
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.3823-3832.2006
Intrarectal immunization with rotavirus 2/6 virus-like particles induces an antirotavirus immune response localized in the intestinal mucosa and protects against rotavirus infection in mice
Abstract
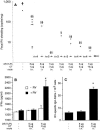
Rotavirus (RV) is the main etiological agent of severe gastroenteritis in infants, and vaccination seems the most effective way to control the disease. Recombinant rotavirus-like particles composed of the viral protein 6 (VP6) and VP2 (2/6-VLPs) have been reported to induce protective immunity in mice when administered by the intranasal (i.n.) route. In this study, we show that administration of 2/6-VLPs by the intrarectal (i.r.) route together with either cholera toxin (CT) or a CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotide as the adjuvant protects adult mice against RV infection. Moreover, when CT is used, RV shedding in animals immunized by the i.r. route is even reduced in comparison with that in animals immunized by the i.n. route. Humoral and cellular immune responses induced by these immunization protocols were analyzed. We found that although i.r. immunization with 2/6-VLPs induces lower RV-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA levels in serum, intestinal anti-RV IgA production is higher in mice immunized by the i.r. route. Cellular immune response has been evaluated by measuring cytokine production by spleen and Peyer's patch cells (PPs) after ex vivo restimulation with RV. Mice immunized by the i.n. and i.r. routes display higher gamma interferon production in spleen and PPs, respectively. In conclusion, we demonstrate that i.r. immunization with 2/6-VLPs protects against RV infection in mice and is more efficient than i.n. immunization in inducing an anti-RV immune response in intestinal mucosa.
Figures



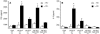
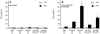
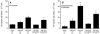
References
-
- Abbas, A. K., K. M. Murphy, and A. Sher. 1996. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 383:787-793. - PubMed
-
- Angel, J., M. A. Franco, H. B. Greenberg, and D. Bass. 1999. Lack of a role for type I and type II interferons in the resolution of rotavirus-induced diarrhea and infection in mice. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 19:655-659. - PubMed
-
- Beagley, K. W., J. H. Eldridge, H. Kiyono, M. P. Everson, W. J. Koopman, T. Honjo, and J. R. McGhee. 1988. Recombinant murine IL-5 induces high rate IgA synthesis in cycling IgA-positive Peyer's patch B cells. J. Immunol. 141:2035-2042. - PubMed
-
- Belyakov, I. M., J. D. Ahlers, B. Y. Brandwein, P. Earl, B. L. Kelsall, B. Moss, W. Strober, and J. A. Berzofsky. 1998. The importance of local mucosal HIV-specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes for resistance to mucosal viral transmission in mice and enhancement of resistance by local administration of IL-12. J. Clin. Investig. 102:2072-2081. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

