Role of vimentin in smooth muscle force development
- PMID: 16571866
- PMCID: PMC1538637
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00097.2006
Role of vimentin in smooth muscle force development
Abstract
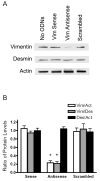
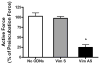
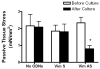
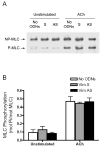
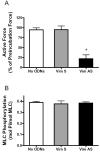
Vimentin intermediate filaments undergo spatial reorganization in cultured smooth muscle cells in response to contractile activation; however, the role of vimentin in the physiological properties of smooth muscle has not been well elucidated. Tracheal smooth muscle strips were loaded with antisense oligonucleotides (ODNs) against vimentin and then cultured for 2 days to allow for protein degradation. Treatment with vimentin antisense, but not sense, ODNs suppressed vimentin protein expression; neither vimentin antisense nor sense ODNs affected protein levels of desmin and actin. Force development in response to ACh stimulation or KCl depolarization was lower in vimentin-deficient tissues than in vimentin sense ODN- or non-ODN-treated muscle strips. Passive tension was also depressed in vimentin-depleted muscle tissues. Vimentin downregulation did not attenuate increases in myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation in response to contractile stimulation or basal MLC phosphorylation. In vimentin sense ODN-treated or non-ODN-treated smooth muscle strips, the desmosomal protein plakoglobin was primarily localized in the cell periphery. The membrane-associated localization of plakoglobin was reduced in vimentin-depleted muscle tissues. These studies suggest that vimentin filaments play an important role in mediating active force development and passive tension, which are not regulated by MLC phosphorylation. Vimentin downregulation impairs the structural organization of desmosomes, which may be associated with the decrease in force development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The focal adhesion protein paxillin regulates contraction in canine tracheal smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2002 Jul 15;542(Pt 2):501-13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.021006. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12122148 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of profilin with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides inhibits force development during stimulation of smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003 Oct;285(4):H1528-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00188.2003. Epub 2003 Jun 12. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12805028
-
Depletion of focal adhesion kinase by antisense depresses contractile activation of smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001 Apr;280(4):C874-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.280.4.C874. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11245605
-
The contractile apparatus and mechanical properties of airway smooth muscle.Eur Respir J. 2000 Mar;15(3):600-16. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.15.29.x. Eur Respir J. 2000. PMID: 10759460 Review.
-
Intermediate filaments in smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Apr;294(4):C869-78. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00154.2007. Epub 2008 Feb 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18256275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polo-like Kinase 1 Regulates Vimentin Phosphorylation at Ser-56 and Contraction in Smooth Muscle.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23693-23703. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.749341. Epub 2016 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27662907 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of β-catenin to N-cadherin is necessary for smooth muscle contraction.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 3;290(14):8913-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621003. Epub 2015 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25713069 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of actin-associated proteins in smooth muscle contraction, cell proliferation, airway hyperresponsiveness and airway remodeling.Respir Res. 2015 Oct 30;16:134. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0296-1. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26517982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and the Basis for Pharmacologic Treatment of Smooth Muscle Disorders.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Apr;68(2):476-532. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.010652. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27037223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular mechanotransduction.Physiol Rev. 2023 Apr 1;103(2):1247-1421. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00053.2021. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36603156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashton FT, Somlyo AV, Somlyo AP. The contractile apparatus of vascular smooth muscle: intermediate high voltage stereo electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1975;98:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Barany M, Barron JT, Gu L, Barany K. Exchange of the actin-bound nucleotide in intact arterial smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:48398–48403. - PubMed
-
- Bornslaeger EA, Godsel LM, Corcoran CM, Park JK, Hatzfeld M, Kowalczyk AP, Green KJ. Plakophilin 1 interferes with plakoglobin binding to desmoplakin, yet together with plakoglobin promotes clustering of desmosomal plaque complexes at cell-cell borders. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:727–738. - PubMed
-
- Chan W, Kozma R, Yasui Y, Inagaki M, Leung T, Manser E, Lim L. Vimentin intermediate filament reorganization by Cdc42: involvement of PAK and p70 S6 kinase. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002;81:692–701. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Goldman RD. Intermediate filaments mediate cytoskeletal crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:601–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

