Ontogenetic distribution of 5-HT2C, 5-HT5A, and 5-HT7 receptors in the rat hippocampus
- PMID: 16572590
- PMCID: PMC6032452
- DOI: 10.3727/000000006783991935
Ontogenetic distribution of 5-HT2C, 5-HT5A, and 5-HT7 receptors in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
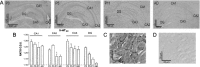
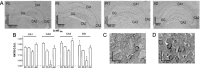
It is known that serotonin exerts its different nociceptive and motor functions by interacting with distinct receptors subtypes, which could be either G-protein coupled or ionotropic. Previous reports demonstrated the early activation of serotonin receptor transcripts during rat development, suggesting a potential role of the serotoninergic system during ontogeny. In this study we have compared the cellular distribution of three serotonin receptor subtypes: 5-HT2C, 5-HT5A, and 5-HT7. Immunocytochemical methods were used in slices of rat hippocampus obtained during the postnatal development. 5-HT2c immunoreactivity was strong at all developmental stages in the CA1 region, whereas differences were observed between P0 and P5 in the CA3 region. The 5-HT5A receptor immunosignal in CA1 and CA3 was strong at P0, decreased at P11, and then increased in the adult. The immunoreactivity to 5-HT7 receptors was high in all regions at P0 and then decreased progressively during postnatal development; the signal was stronger for 5-HT2c than for 5-HT5A and 5-HT7 receptors. Changes in the expression level of each receptor may result in differences in functional and pharmacological properties of the cells expressing them as well as in the hippocampal neuronal network. The distribution of the three serotonin receptor subtypes studied varied during the ontogeny, which supports their potential role during development and will help to understand their mechanisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of hippocampal serotonin receptors 5-HT2C and 5-HT5A in a rat model of diet-induced obesity supplemented with tryptophan.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2015 May;42:80-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2015.02.010. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25720309
-
Serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT5A receptors are expressed by different motoneuron populations in rat Onuf's nucleus.J Comp Neurol. 2007 Jun 1;502(4):620-34. doi: 10.1002/cne.21344. J Comp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17394137
-
Postnatal development of serotonin 1B, 2 A and 2C receptors in brainstem motoneurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Mar;17(6):1179-88. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02545.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12670306
-
Studies on the neuroendocrine role of serotonin.Dan Med Bull. 2007 Nov;54(4):266-88. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 18208678 Review.
-
Serotonin Receptor Binding Characteristics of Geissoschizine Methyl Ether, an Indole Alkaloid in Uncaria Hook.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(9):1036-1045. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170320114713. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28322152 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of serotonin in the hippocampus: how SSRIs and multimodal antidepressants might regulate pyramidal cell function.CNS Spectr. 2016 Apr;21(2):143-61. doi: 10.1017/S1092852915000425. Epub 2015 Sep 8. CNS Spectr. 2016. PMID: 26346726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin Modulation of Dorsoventral Hippocampus in Physiology and Schizophrenia.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 27;26(15):7253. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157253. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescent male rats are less sensitive than adults to the anxiogenic and serotonin-releasing effects of fenfluramine.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Feb;65:213-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.10.010. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23103347 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-HT(7) receptor in learning and memory.Hippocampus. 2012 Apr;22(4):762-71. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20938. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Hippocampus. 2012. PMID: 21484935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin receptors in hippocampus.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:823493. doi: 10.1100/2012/823493. Epub 2012 May 2. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22629209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnes N. M.; Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38:1083–1152; 1999. - PubMed
-
- Brezun J. M.; Daszuta A. Depletion in serotonin decreases neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus and the sub-ventricular zone of adult rats. Neuroscience 89:999–1002; 1999. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter M. K.; Parker I.; Miledi R. Changes in messenger RNAs coding for neurotransmitter receptors and voltage-operated channels in the developing rat cerebral cortex. Dev. Biol. 138(2):313–323; 1990. - PubMed
-
- Carson M. J.; Thomas E. A.; Danielson P. E.; Sutcliffe J. G. The 5-HT5A serotonin receptor is expressed predominantly by astrocytes in which it inhibits cAMP accumulation: A mechanism for neuronal suppression of reactive astrocytes. Glia 17:317–326; 1996. - PubMed
-
- Clemett D. A.; Punhani T.; Duxon M. S.; Blackburn T. P.; Fone K. C. Immunohistochemical localisation of the 5-HT2C receptor protein in the rat CNS. Neuropharmacology 39:123–132; 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
