Inhibition of apoptosis by p26: implications for small heat shock protein function during Artemia development
- PMID: 16572731
- PMCID: PMC1400614
- DOI: 10.1379/csc-154r.1
Inhibition of apoptosis by p26: implications for small heat shock protein function during Artemia development
Abstract
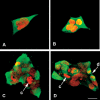
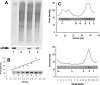
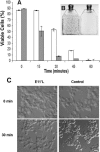
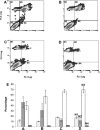
p26, an abundantly expressed small heat shock protein, is thought to establish stress resistance in oviparously developing embryos of the crustacean Artemia franciscana by preventing irreversible protein denaturation, but it might also promote survival by inhibiting apoptosis. To test this possibility, stably transfected mammalian cells producing p26 were generated and their ability to resist apoptosis induction determined. Examination of immunofluorescently stained transfected 293H cells by confocal microscopy demonstrated p26 is diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm with a minor amount of the protein in nuclei. As shown by immunoprobing of Western blots, p26 constituted approximately 0.6% of soluble cell protein. p26 localization and quantity were unchanged during prolonged culture, and the protein had no apparent ill effects on transfected cells. Molecular sieve chromatography in Sepharose 6B revealed p26 oligomers of about 20 monomers, with a second fraction occurring as larger aggregates. A similar pattern was observed in sucrose gradients, but overall oligomer size was smaller. Mammalian cells containing p26 were more thermotolerant than cells transfected with the expression vector only, and as measured by annexin V labeling, Hoescht 33342 nuclear staining and procaspase-3 activation, transfected cells effectively resisted apoptosis induction by heat and staurosporine. The ability to confer thermotolerance and limit heat-induced apoptosis is important because Artemia embryos are frequently exposed to high temperature in their natural habitat. p26 also blocked apoptosis in transfected cells during drying and rehydration, findings with direct relevance to Artemia life history characteristics because desiccation terminates cyst diapause. Thus, in addition to functioning as a molecular chaperone, p26 inhibits apoptosis, an activity shared by other small heat shock proteins and with the potential to play an important role during Artemia embryo development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stress tolerance during diapause and quiescence of the brine shrimp, Artemia.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016 Jan;21(1):9-18. doi: 10.1007/s12192-015-0635-7. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016. PMID: 26334984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligomerization, chaperone activity, and nuclear localization of p26, a small heat shock protein from Artemia franciscana.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 17;279(38):39999-40006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406999200. Epub 2004 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15258152
-
Structural and functional roles for beta-strand 7 in the alpha-crystallin domain of p26, a polydisperse small heat shock protein from Artemia franciscana.FEBS J. 2006 Mar;273(5):1020-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05129.x. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16478475
-
Molecular characterization of a small heat shock/alpha-crystallin protein in encysted Artemia embryos.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jul 25;272(30):19051-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.30.19051. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9228089
-
Molecular chaperones, stress resistance and development in Artemia franciscana.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2003 Oct;14(5):251-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.09.019. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 14986854 Review.
Cited by
-
Anhydrobiosis-associated nuclear DNA damage and repair in the sleeping chironomid: linkage with radioresistance.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 16;5(11):e14008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014008. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21103355 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Purified Artemia Extract Proteins on Proliferation, Differentiation and Apoptosis of Human Leukemic HL-60 Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016 Dec 1;17(12):5139-5145. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2016.17.12.5139. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016. PMID: 28122447 Free PMC article.
-
The small heat shock protein p26 aids development of encysting Artemia embryos, prevents spontaneous diapause termination and protects against stress.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43723. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043723. Epub 2012 Aug 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952748 Free PMC article.
-
Stress tolerance during diapause and quiescence of the brine shrimp, Artemia.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016 Jan;21(1):9-18. doi: 10.1007/s12192-015-0635-7. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016. PMID: 26334984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermally induced and developmentally regulated expression of a small heat shock protein in Trichinella spiralis.Parasitol Res. 2007 Jun;101(1):201-12. doi: 10.1007/s00436-007-0462-6. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Parasitol Res. 2007. PMID: 17268805
References
-
- Bruey J-M, Ducasse C, and Bonniaud P. et al. 2000 Hsp27 negatively regulates cell death by interacting with cytochrome c. Nat Cell Biol. 2:645–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
