Effect of myocardial reperfusion on the release of nitric oxide after regional ischemia: an experimental model of beating-heart surgery
- PMID: 16572867
- PMCID: PMC1413597
Effect of myocardial reperfusion on the release of nitric oxide after regional ischemia: an experimental model of beating-heart surgery
Abstract
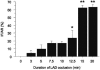
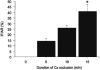
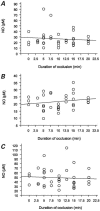
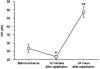
Off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery is increasing in popularity worldwide. However, very little is known about the effect of regional myocardial ischemia-reperfusion on nitric oxide release. In an animal model mimicking off-pump bypass, male Sprague-Dawley rats (350-450 g) were mechanically ventilated under general anesthesia. After left lateral thoracotomy, the animals underwent occlusion of either the left anterior descending artery (for 3, 5, 75, 10, 12.5, 15, or 20 minutes) or the circumflex artery (for 5, 10, or 15 minutes). Twenty-four hours after reperfusion, heart tissue was stained for determination of the area at risk and the infarcted area. Blood samples obtained before ischemia, 10 minutes after reperfusion, and 24 hours after reperfusion were analyzed for plasma concentrations of nitric oxide. After occlusion of the left anterior descending artery, the size of the infarcted area increased dramatically as the duration of occlusion increased, and was significantly larger after 12.5, 15, or 20 minutes of occlusion than after 3 minutes. After occlusion of the circumflex artery, the size of the infarcted area increased steadily and was significantly larger after 15 minutes of occlusion than after 5 minutes. There was no significant correlation between the duration of coronary occlusion and the plasma concentration of nitric oxide: 10 minutes after reperfusion, this concentration was significantly lower than that before ischemia, but it was twice the baseline level 24 hours after reperfusion. We concluded that the duration of regional ischemia did not affect the plasma concentration of nitric oxide in the systemic circulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute effect of cerivastatin on cardiac regional ischemia in a rat model mimicking off-pump coronary surgery.J Card Surg. 2005 Nov-Dec;20(6):507-11; discussion 512. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8191.2005.00139.x. J Card Surg. 2005. PMID: 16309399
-
Free radical reaction products and antioxidant capacity in beating heart coronary artery surgery compared to conventional bypass.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011 Jun;76(6):677-85. doi: 10.1134/S0006297911060083. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011. PMID: 21639848
-
Effect of desflurane-induced preconditioning following ischemia-reperfusion on nitric oxide release in rabbits.Life Sci. 2004 Dec 24;76(6):651-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.05.025. Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15567190
-
Clematichinenoside attenuates myocardial infarction in ischemia/reperfusion injury both in vivo and in vitro.Planta Med. 2013 Sep;79(14):1289-97. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1350671. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Planta Med. 2013. PMID: 23929248
-
Remote postconditioning. Brief renal ischemia and reperfusion applied before coronary artery reperfusion reduces myocardial infarct size via endogenous activation of adenosine receptors.Basic Res Cardiol. 2005 Sep;100(5):404-12. doi: 10.1007/s00395-005-0539-2. Epub 2005 Jun 17. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 15965583
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular MR T2-STIR imaging does not discriminate between intramyocardial haemorrhage and microvascular obstruction during the subacute phase of a reperfused myocardial infarction.Open Heart. 2016 Apr 20;3(1):e000346. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2015-000346. eCollection 2016. Open Heart. 2016. PMID: 27110375 Free PMC article.
-
Volatile anesthetic preconditioning modulates oxidative stress and nitric oxide in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting.Ann Card Anaesth. 2021 Jul-Sep;24(3):319-326. doi: 10.4103/aca.ACA_130_20. Ann Card Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 34269262 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Yacoub M. Off-pump coronary bypass surgery: in search of an identity. Circulation 2001;104:1743–5. - PubMed
-
- Anyanwu AC, Al-Ruzzeh S, George SJ, Patel R, Yacoub MH, Amrani M. Conversion to off-pump coronary bypass without increased morbidity or change in practice. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:798–802. - PubMed
-
- Amrani M, Chester AH, Jayakumar J, Schyns CJ, Yacoub MH. L-arginine reverses low coronary reflow and enhances postischemic recovery of cardiac mechanical function. Cardiovasc Res 1995;30:200–4. - PubMed
-
- Amrani M, Gray CC, Smolenski RT, Goodwin AT, London A, Yacoub MH. The effect of L-arginine on myocardial recovery after cardioplegic arrest and ischemia under moderate and deep hypothermia. Circulation 1997;96(9 Suppl):II-274–9. - PubMed
-
- Pernow J, Uriuda Y, Wang QD, Li XS, Nordlander R, Rydeen L. The protective effect of L-arginine on myocardial injury and endothelial function following ischaemia and reperfusion in the pig. Eur Heart J 1994;15:1712–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
