The future of antisense oligonucleotides in the treatment of respiratory diseases
- PMID: 16573347
- PMCID: PMC7100773
- DOI: 10.2165/00063030-200620010-00001
The future of antisense oligonucleotides in the treatment of respiratory diseases
Abstract
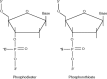
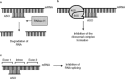
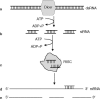
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) are short synthetic DNA molecules designed to inhibit translation of a targeted gene to protein via interaction with messenger RNA. More recently, small interfering (si)RNA have been developed as potent tools to specifically inhibit gene expression. ASO directed against signaling molecules, cytokine receptors, and transcription factors involved in allergic immune and inflammatory responses, have been applied in experimental models of asthma and demonstrate potential as therapeutics. Several ASO-based drugs directed against oncogenes have been developed for therapy of lung cancer, and some have recently reached clinical trials. ASO and siRNA to respiratory syncytial virus infection have demonstrated good potential to treat this condition, particularly in combination with an antiviral drug. Although ASO-based therapeutics are promising for lung diseases, issues of specificity, identification of correct molecular targets, delivery and carrier systems, as well as potential adverse effects must be carefully evaluated before clinical application.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety of antisense oligonucleotide and siRNA-based therapeutics.Drug Discov Today. 2017 May;22(5):823-833. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Drug Discov Today. 2017. PMID: 28159625 Review.
-
Antisense molecules for targeted cancer therapy.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006 Jul;59(1):65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2005.10.004. Epub 2006 Jun 5. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006. PMID: 16750913 Review.
-
Respirable antisense oligonucleotides: a new, third drug class targeting respiratory disease.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002 Dec;2(6):533-6. doi: 10.1097/00130832-200212000-00009. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. PMID: 14752337 Review.
-
Oligonucleotide Therapy for Obstructive and Restrictive Respiratory Diseases.Molecules. 2017 Jan 17;22(1):139. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010139. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28106744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of dyslipidaemia.Eur Heart J. 2012 Jun;33(12):1451-8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs084. Epub 2012 May 24. Eur Heart J. 2012. PMID: 22634577 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogel armed with Bmp2 mRNA-enriched exosomes enhances bone regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Apr 5;21(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01871-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37020301 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of antisense transcription initiation from the 3' end of the GAL10 coding sequence in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;33(18):3549-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01715-12. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23836882 Free PMC article.
-
Gene silencing in the therapy of influenza and other respiratory diseases: Targeting to RNase P by use of External Guide Sequences (EGS).Biologics. 2007 Dec;1(4):425-32. Biologics. 2007. PMID: 19707312 Free PMC article.
-
Versatility of Liposomes for Antisense Oligonucleotide Delivery: A Special Focus on Various Therapeutic Areas.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 8;15(5):1435. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051435. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Antisense Transcription Initiation with Implications in Gene Expression, Genomic Integrity and Disease Pathogenesis.Noncoding RNA. 2019 Jan 21;5(1):11. doi: 10.3390/ncrna5010011. Noncoding RNA. 2019. PMID: 30669611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mercatante D.R., Kole R. Control of alternative splicing by antisense oligonucleotides as a potential chemotherapy: effects on gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1587(2–3):126–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

