Characterizing the flagellar filament and the role of motility in bacterial prey-penetration by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus
- PMID: 16573680
- PMCID: PMC1453311
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05081.x
Characterizing the flagellar filament and the role of motility in bacterial prey-penetration by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus
Abstract
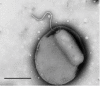
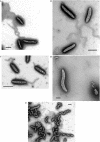
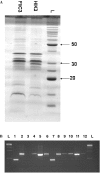
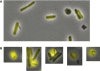
The predatory bacterium Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus swims rapidly by rotation of a single, polar flagellum comprised of a helical filament of flagellin monomers, contained within a membrane sheath and powered by a basal motor complex. Bdellovibrio collides with, enters and replicates within bacterial prey, a process previously suggested to firstly require flagellar motility and then flagellar shedding upon prey entry. Here we show that flagella are not always shed upon prey entry and we study the six fliC flagellin genes of B. bacteriovorus, finding them all conserved and expressed in genome strain HD100 and the widely studied lab strain 109J. Individual inactivation of five of the fliC genes gave mutant Bdellovibrio that still made flagella, and which were motile and predatory. Inactivation of the sixth fliC gene abolished normal flagellar synthesis and motility, but a disordered flagellar sheath was still seen. We find that this non-motile mutant was still able to predate when directly applied to lawns of YFP-labelled prey bacteria, showing that flagellar motility is not essential for prey entry but important for efficient encounters with prey in liquid environments.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Three motAB stator gene products in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus contribute to motility of a single flagellum during predatory and prey-independent growth.J Bacteriol. 2011 Feb;193(4):932-43. doi: 10.1128/JB.00941-10. Epub 2010 Dec 10. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21148728 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of multiple flagellins in flagellar formation and flagellar growth post bdelloplast lysis in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus.J Mol Biol. 2009 Dec 18;394(5):1011-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.10.003. Epub 2009 Oct 9. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19819245 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of a simultaneously predatory and prey-independent, novel Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus from the River Tiber, supports in silico predictions of both ancient and recent lateral gene transfer from diverse bacteria.BMC Genomics. 2012 Nov 27;13:670. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-670. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23181807 Free PMC article.
-
A predatory patchwork: membrane and surface structures of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus.Adv Microb Physiol. 2009;54:313-61. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2911(08)00005-2. Adv Microb Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18929071 Review.
-
Polar flagellar motility of the Vibrionaceae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001 Sep;65(3):445-62, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.65.3.445-462.2001. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11528005 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into the Possible Use of the Predator Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus as a Probiotic.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 28;12(8):2252. doi: 10.3390/nu12082252. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32731403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To hunt or to rest: prey depletion induces a novel starvation survival strategy in bacterial predators.ISME J. 2021 Jan;15(1):109-123. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00764-2. Epub 2020 Sep 3. ISME J. 2021. PMID: 32884113 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptional "Scream" early response of E. coli prey to predatory invasion by Bdellovibrio.Curr Microbiol. 2010 Jun;60(6):419-27. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9559-8. Epub 2009 Dec 20. Curr Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20024656 Free PMC article.
-
Cyanide Production by Chromobacterium piscinae Shields It from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus HD100 Predation.mBio. 2017 Dec 19;8(6):e01370-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01370-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29259082 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of novel Pseudobdellovibrionaceae genera and species yields insights into the genomics and evolution of bacterial predation mode.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 20:2025.02.19.638989. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.19.638989. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40027812 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Bierman M, Logan R, O'Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE. Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene. 1992;116:43–49. - PubMed
-
- Gomelsky L, Sram J, Moskvin OV, Horne IM, Dodd HN, Pemberton JM, et al. Identification and in vivo characterization of PpaA, a regulator of photosystem formation in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Microbiology. 2003;149:377–388. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983;166:557–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

