Changes in flagellin glycosylation affect Campylobacter autoagglutination and virulence
- PMID: 16573682
- PMCID: PMC1424674
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05100.x
Changes in flagellin glycosylation affect Campylobacter autoagglutination and virulence
Abstract
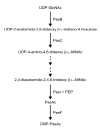
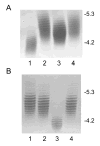
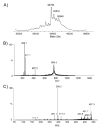
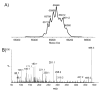
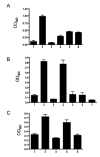
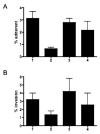
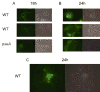
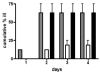
Analysis of the complete flagellin glycosylation locus of Campylobacter jejuni strain 81-176 revealed a less complex genomic organization than the corresponding region in the genome strain, C. jejuni NCTC 11168. Twenty-four of the 45 genes found between Cj1293 and Cj1337 in NCTC 11168 are missing in 81-176. Mutation of six new genes, in addition to three previously reported, resulted in a non-motile phenotype, consistent with a role in synthesis of pseudaminic acid (PseAc) or transfer of PseAc to flagellin. Mutation of Cj1316c or pseA had been shown to result in loss of the acetamidino form of pseudaminic acid (PseAm). Mutation of a second gene also resulted in loss of PseAm, as well as a minor modification that appears to be PseAm extended with N-acetyl-glutamic acid. Previously described mutants in C. jejuni 81-176 and Campylobacter coli VC167 that produced flagella lacking PseAm or PseAc failed to autoagglutinate. This suggests that interactions between modifications on adjacent flagella filaments are required for autoagglutination. Mutants (81-176) defective in autoagglutination showed a modest reduction in adherence and invasion of INT407 cells. However, there was a qualitative difference in binding patterns to INT407 cells using GFP-labelled 81-176 and mutants lacking PseAm. A mutant lacking PseAm was attenuated in the ferret diarrhoeal disease model.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pseudaminic acid, the major modification on Campylobacter flagellin, is synthesized via the Cj1293 gene.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Oct;50(2):659-71. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03725.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14617187
-
Structural heterogeneity of carbohydrate modifications affects serospecificity of Campylobacter flagellins.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Oct;46(2):587-97. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03185.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12406231
-
Functional characterization of the flagellar glycosylation locus in Campylobacter jejuni 81-176 using a focused metabolomics approach.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 7;281(27):18489-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603777200. Epub 2006 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16684771
-
Flagellin glycosylation with pseudaminic acid in Campylobacter and Helicobacter: prospects for development of novel therapeutics.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Apr;75(7):1163-1178. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2696-5. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29080090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Campylobacter flagella: not just for motility.Trends Microbiol. 2007 Oct;15(10):456-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.09.006. Epub 2007 Oct 24. Trends Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17920274 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of motility and biofilm formation by intestinal Campylobacter concisus strains.Gut Pathog. 2012 Dec 14;4(1):22. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-4-22. Gut Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23241133 Free PMC article.
-
Cj1388 Is a RidA Homolog and Is Required for Flagella Biosynthesis and/or Function in Campylobacter jejuni.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 6;10:2058. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02058. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31555246 Free PMC article.
-
Protein glycosylation in Campylobacter jejuni: partial suppression of pglF by mutation of pseC.J Bacteriol. 2007 Sep;189(18):6731-3. doi: 10.1128/JB.00642-07. Epub 2007 Jul 13. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17631632 Free PMC article.
-
Gram-negative flagella glycosylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Feb 19;15(2):2840-57. doi: 10.3390/ijms15022840. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24557579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation of DsbA in Francisella tularensis subsp. tularensis.J Bacteriol. 2011 Oct;193(19):5498-509. doi: 10.1128/JB.00438-11. Epub 2011 Jul 29. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21803994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacon DJ, Szymanski CM, Burr DH, RP Silver RP, Alm RA, Guerry P. A phase variable capsule is involved in virulence of Campylobacter jejuni 81–176. Mol Microbiol. 2001;40:769–777. - PubMed
-
- Benz I, Schmidt MA. Glycoylation with heptose residues mediated by the aah gene product is essential for adherence of the AIDA adhesin. Mol Microbiol. 2001;40:1403–1413. - PubMed
-
- Bieber D, Ramer SW, Wu CY, Murray WJ, Tobe T, Fernandez R, Schoolnik GK. Type IV pili, transient bacterial aggregates, and virulence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Science. 1998;280:2114–2118. - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Levine MM, Clements ML, Hughes TP, Blaser MJ. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988;157:472–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

