Protocol for the Arterial Revascularisation Trial (ART). A randomised trial to compare survival following bilateral versus single internal mammary grafting in coronary revascularisation [ISRCTN46552265]
- PMID: 16573820
- PMCID: PMC1450314
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-7-7
Protocol for the Arterial Revascularisation Trial (ART). A randomised trial to compare survival following bilateral versus single internal mammary grafting in coronary revascularisation [ISRCTN46552265]
Abstract
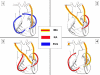
Background: Standard coronary artery bypass graft surgery uses a single internal mammary artery and supplemental vein or radial artery grafts. Several observational studies have suggested a survival benefit with two internal mammary artery grafts compared to a single internal mammary artery graft, but this has not been tested in a randomised trial. The Arterial Revascularisation Trial is a Medical Research Council and British Heart Foundation funded, multi-centre international trial comparing single internal mammary artery grafting versus bilateral internal mammary artery grafting.
Methods/design: Twenty centres in the UK, Australia, Poland and Brazil are planning to randomise 3000 coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients to single or bilateral internal mammary artery grafting. Supplemental grafts may be either saphenous vein or radial artery. Coronary artery bypass grafting can be performed as an on-pump or off-pump procedure. The primary outcome is survival at 10 years and secondary end-points include clinical events, quality of life and cost effectiveness. The effect of age, left ventricular function, diabetes, number of grafts, vein grafts and off-pump surgery are pre-specified subgroups.
Discussion: The Arterial Revascularisation Trial is one of the first randomised trials to evaluate the effects on survival and other clinical outcomes of single internal mammary artery grafting versus bilateral internal mammary artery grafting, and will help to establish the best approach for patients requiring coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Figures

References
-
- Keogh BE, Kinsman R. National Adult Cardiac Surgical Database Report 1999–2001.
-
- Loop FD, Lytle BW, Cosgrove DM, et al. Influence of the internal mammary artery graft on 10-year survival and other cardiac events. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:1–6. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

