Prototypical antipsychotic drugs protect hippocampal neuronal cultures against cell death induced by growth medium deprivation
- PMID: 16573831
- PMCID: PMC1448194
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-28
Prototypical antipsychotic drugs protect hippocampal neuronal cultures against cell death induced by growth medium deprivation
Abstract
Background: Several clinical studies suggested that antipsychotic-based medications could ameliorate cognitive functions impaired in certain schizophrenic patients. Accordingly, we investigated the effects of various dopaminergic receptor antagonists--including atypical antipsychotics that are prescribed for the treatment of schizophrenia--in a model of toxicity using cultured hippocampal neurons, the hippocampus being a region of particular relevance to cognition.
Results: Hippocampal cell death induced by deprivation of growth medium constituents was strongly blocked by drugs including antipsychotics (10(-10)-10(-6) M) that display nM affinities for D2 and/or D4 receptors (clozapine, haloperidol, (+/-)-sulpiride, domperidone, clozapine, risperidone, chlorpromazine, (+)-butaclamol and L-741,742). These effects were shared by some caspases inhibitors and were not accompanied by inhibition of reactive oxygen species. In contrast, (-)-raclopride and remoxipride, two drugs that preferentially bind D2 over D4 receptors were ineffective, as well as the selective D3 receptor antagonist U 99194. Interestingly, (-)-raclopride (10(-6) M) was able to block the neuroprotective effect of the atypical antipsychotic clozapine (10(-6) M).
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggest that D2-like receptors, particularly the D4 subtype, mediate the neuroprotective effects of antipsychotic drugs possibly through a ROS-independent, caspase-dependent mechanism.
Figures

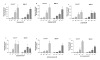

References
-
- Seeman P. Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1980;32:229–313. - PubMed
-
- Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH. Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science. 1976;192:481–483. - PubMed
-
- King DJ. The effect of neuroleptics on cognitive and psychomotor function. Br J Psychiatry. 1980;157:799–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

