Extensive adenosine-to-inosine editing detected in Alu repeats of antisense RNAs reveals scarcity of sense-antisense duplex formation
- PMID: 16574103
- PMCID: PMC2944036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.03.042
Extensive adenosine-to-inosine editing detected in Alu repeats of antisense RNAs reveals scarcity of sense-antisense duplex formation
Abstract
One type of RNA editing converts adenosine residues to inosine in double-stranded regions. Recent transcriptome analysis has revealed that numerous Alu repeats, present within introns and untranslated regions of human transcripts, are subject to this A-->I RNA editing. Furthermore, it revealed global transcription of antisense RNAs. Here, we demonstrate that antisense RNAs are also edited extensively but only in their Alu repeat sequences, and editing does not extend to the surrounding sequence. Our findings imply that sense and antisense RNAs form two separate intramolecular double-stranded RNAs consisting of inversely oriented Alu repeats, but rarely form intermolecular duplexes.
Figures

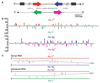
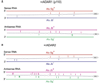
Similar articles
-
Identification of widespread ultra-edited human RNAs.PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002317. Epub 2011 Oct 20. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22028664 Free PMC article.
-
Is there any sense in antisense editing?Trends Genet. 2005 Oct;21(10):544-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2005.08.005. Trends Genet. 2005. PMID: 16099531
-
Cutting Edge: Reduced Adenosine-to-Inosine Editing of Endogenous Alu RNAs in Severe COVID-19 Disease.J Immunol. 2021 Apr 15;206(8):1691-1696. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2001428. Epub 2021 Mar 29. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33782089 Free PMC article.
-
Letter from the editor: Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing in Alu repeats in the human genome.EMBO Rep. 2005 Sep;6(9):831-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400507. EMBO Rep. 2005. PMID: 16138094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALU A-to-I RNA Editing: Millions of Sites and Many Open Questions.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2181:149-162. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0787-9_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32729079 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for large diversity in the human transcriptome created by Alu RNA editing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Nov;37(20):6905-15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp729. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19740767 Free PMC article.
-
Recognize Yourself-Innate Sensing of Non-LTR Retrotransposons.Viruses. 2021 Jan 12;13(1):94. doi: 10.3390/v13010094. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33445593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous Double-Stranded RNA.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Feb 19;7(1):15. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7010015. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 33669629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zα and Zβ Localize ADAR1 to Flipons That Modulate Innate Immunity, Alternative Splicing, and Nonsynonymous RNA Editing.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 7;26(6):2422. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062422. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intronic Alus influence alternative splicing.PLoS Genet. 2008 Sep 26;4(9):e1000204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000204. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18818740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keegan LP, Gallo A, O’Connell MA. The many roles of an RNA editor. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001;2:869–878. - PubMed
-
- Maas S, Rich A, Nishikura K. A-to-I RNA editing: recent news and residual mysteries. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:1391–1394. - PubMed
-
- Seeburg PH, Hartner J. Regulation of ion channel/neurotransmitter receptor function by RNA editing. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003;13:279–283. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi M, Single FN, Köhler M, Sommer B, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH. RNA editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR-B: a base-paired intron–exon structure determines position and efficiency. Cell. 1993;75:1361–1370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

