Regulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 pleckstrin homology domain by protein kinase C: role of serine 24 phosphorylation
- PMID: 16574739
- PMCID: PMC4303764
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2005-0536
Regulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 pleckstrin homology domain by protein kinase C: role of serine 24 phosphorylation
Abstract
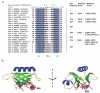
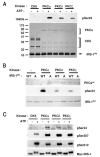
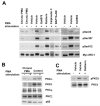
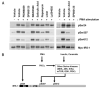
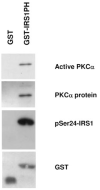
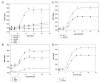
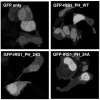
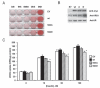
Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins on serine residues is an important posttranslational modification that is linked to insulin resistance. Several phosphoserine sites on IRS1 have been identified; the majority are located proximal to the phosphotryosine-binding domain or near key receptor tyrosine kinase substrate- and/or Src-homology 2 domain-binding sites. Here we report on the characterization of a serine phosphorylation site in the N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of IRS1. Bioinformatic tools identify serine 24 (Ser24) as a putative substrate site for the protein kinase C (PKC) family of serine kinases. We demonstrate that this site is indeed a bona fide substrate for conventional PKC. In vivo, IRS-1 is also phosphorylated on Ser24 after phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate treatment of cells, and isoform-selective inhibitor studies suggest the involvement of PKCalpha. By comparing the pharmacological characteristics of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-stimulated Ser24 phosphorylation with phosphorylation at two other sites previously linked to PKC activity (Ser307 and Ser612), we show that PKCalpha is likely to be directly involved in Ser24 phosphorylation, but indirectly involved in Ser307 and Ser612 phosphorylation. Using Ser24Asp IRS-1 mutants to mimic the phosphorylated residue, we demonstrate that the phosphorylation status of Ser24 does play an important role in regulating phosphoinositide binding to, and the intracellular localization of, the IRS1-PH domain, which can ultimately impinge on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. Hence we provide evidence that IRS1-PH domain function is important for normal insulin signaling and is regulated by serine phosphorylation in a manner that could contribute to insulin resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of Ser24 in the pleckstrin homology domain of insulin receptor substrate-1 by Mouse Pelle-like kinase/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase: cross-talk between inflammatory signaling and insulin signaling that may contribute to insulin resistance.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 17;280(24):23173-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501439200. Epub 2005 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15849359
-
Protein kinase C isoforms alpha, delta and theta require insulin receptor substrate-1 to inhibit the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in human kidney embryonic cells (HEK 293 cells).Diabetologia. 1998 Jul;41(7):833-8. doi: 10.1007/s001250050995. Diabetologia. 1998. PMID: 9686926
-
Salicylic acid reverses phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)- and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha)-induced insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) serine 307 phosphorylation and insulin resistance in human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 3;278(1):180-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205565200. Epub 2002 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12409308
-
Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling through IRS-1 phosphorylation.Biochimie. 2005 Jan;87(1):99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.10.019. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 15733744 Review.
-
Fatty acid-induced insulin resistance: role of insulin receptor substrate 1 serine phosphorylation in the retroregulation of insulin signalling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Dec;31(Pt 6):1152-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0311152. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 14641015 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin and metabolic stress stimulate multisite serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 and inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 2;289(18):12467-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554162. Epub 2014 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24652289 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation Codes in IRS-1 and IRS-2 Are Associated with the Activation/Inhibition of Insulin Canonical Signaling Pathways.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 9;46(1):634-649. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010041. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase C function in muscle, liver, and beta-cells and its therapeutic implications for type 2 diabetes.Diabetes. 2008 Jul;57(7):1774-83. doi: 10.2337/db07-1769. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18586909 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Unraveling the Mystery of Insulin Resistance: From Principle Mechanistic Insights and Consequences to Therapeutic Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2770. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062770. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enforced expression of protein kinase C in skeletal muscle causes physical inactivity, fatty liver and insulin resistance in the brain.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Apr;14(4):903-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00629.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20569275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zick Y. Uncoupling insulin signalling by serine/threonine phosphorylation: a molecular basis for insulin resistance. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004;32:812–816. - PubMed
-
- Lee YH, White MF. Insulin receptor substrate proteins and diabetes. Arch Pharm Res. 2004;27:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Voliovitch H, Schindler DG, Hadari YR, Taylor SI, Accili D, Zick Y. Tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 in vivo depends upon the presence of its pleckstrin homology region. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18083–18087. - PubMed
-
- Myers MG, Jr, Grammer TC, Brooks J, Glasheen EM, Wang LM, Sun XJ, Blenis J, Pierce JH, White MF. The pleckstrin homology domain in insulin receptor substrate-1 sensitizes insulin signaling. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:11715–11718. - PubMed
-
- White MF. IRS proteins and the common path to diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;283:E413–E422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

