Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induces a novel transcription factor that causes cardiac myocyte apoptosis and ventricular dysfunction
- PMID: 16574901
- PMCID: PMC1523425
- DOI: 10.1161/01.RES.0000220106.64661.71
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induces a novel transcription factor that causes cardiac myocyte apoptosis and ventricular dysfunction
Abstract
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1; CCL2)-mediated inflammation plays a critical role in the development of ischemic heart disease (IHD). However, the gene expression changes caused by signal transduction, triggered by MCP-1 binding to its receptor CCR2, and their possible role in the development of IHD are not understood. We present evidence that MCP-1 binding to CCR2 induces a novel transcription factor (MCP-induced protein [MCPIP]) that causes cell death. Gene microarray analysis showed that when expressed in hiuman embryonic kidney 293 cells, MCPIP induced apoptotic gene families before causing cell death. Mutagenesis studies showed that the structural features required for transcription factor-like activity were also required for causing cell death. Activation of caspase-3 was detected after MCPIP transfection and Z-VAD-fmk partially inhibited cell death. Cardiomyocyte-targeted expression of MCP-1 in mice caused death by heart failure at 6 months of age. MCPIP expression increased in parallel with the development of ventricular dysfunction. In situ hybridization showed the presence of MCPIP transcripts in the cardiomyocytes and immunohistochemistry showed that MCPIP was associated with the cardiomyocyte nuclei of apoptotic cardiomyocytes. CCR2 expression in cardiomyocytes increased with the development of IHD. MCPIP production induced by MCP-1 binding to CCR2 in the cardiomyocytes is probably involved in the development of IHD in this murine model. MCPIP transcript levels were much higher in the explanted human hearts with IHD than with nonischemic heart disease. These results provide a molecular insight into how chronic inflammation and exposure to MCP-1 contributes to heart failure and suggest that MCPIP could be a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
Figures


 ) and GFP alone (▪). Cells were transfected with MCPIP–GFP or GFP alone, harvested at either day 1 or day 5 after transfection, >200 cells were examined for each time point, and experiments were repeated four times. Cell death was detected by TUNEL and trypan blue. C, Immunoblot analysis of PARP cleavage in HEK293 cells transfected with MCPIP–GFP and GFP alone using PARP antibodies from Abcam. D, Immunoblot analysis of caspase-3 species recovered with avidin after labeling the active caspases with biotin-Z-VAD-fmk showing caspase-3 activation. The inhibitor treatment was done 3 days after transfection, and the blots were quantified by densitometry. E, Inhibition of HEK293 death induced by MCPIP by Z-VAD-fmk. *P<0.05
) and GFP alone (▪). Cells were transfected with MCPIP–GFP or GFP alone, harvested at either day 1 or day 5 after transfection, >200 cells were examined for each time point, and experiments were repeated four times. Cell death was detected by TUNEL and trypan blue. C, Immunoblot analysis of PARP cleavage in HEK293 cells transfected with MCPIP–GFP and GFP alone using PARP antibodies from Abcam. D, Immunoblot analysis of caspase-3 species recovered with avidin after labeling the active caspases with biotin-Z-VAD-fmk showing caspase-3 activation. The inhibitor treatment was done 3 days after transfection, and the blots were quantified by densitometry. E, Inhibition of HEK293 death induced by MCPIP by Z-VAD-fmk. *P<0.05

 ) and decrease in fractional shortening (C). Gene expression was measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
) and decrease in fractional shortening (C). Gene expression was measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR.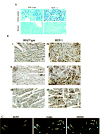

 ) and wild-type mice (▪; A) and in situ hybridization showing expression of CCR2 in cardiomyocytes in 6-month-old of MCP-1 mice (B). *P<0.05 vs wild-type (n = 6 each group).
) and wild-type mice (▪; A) and in situ hybridization showing expression of CCR2 in cardiomyocytes in 6-month-old of MCP-1 mice (B). *P<0.05 vs wild-type (n = 6 each group).Comment in
-
MCP-1 induces a novel transcription factor with proapoptotic activity.Circ Res. 2006 May 12;98(9):1107-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000223483.12225.80. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16690887 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Hyperglycaemia-induced cardiomyocyte death is mediated via MCP-1 production and induction of a novel zinc-finger protein MCPIP.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Sep 1;87(4):665-74. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq102. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20356868 Free PMC article.
-
MCP-1 causes cardiomyoblast death via autophagy resulting from ER stress caused by oxidative stress generated by inducing a novel zinc-finger protein, MCPIP.Biochem J. 2010 Jan 27;426(1):43-53. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090976. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 19925454
-
MCP-1-induced protein attenuates post-infarct cardiac remodeling and dysfunction through mitigating NF-κB activation and suppressing inflammation-associated microRNA expression.Basic Res Cardiol. 2015 May;110(3):26. doi: 10.1007/s00395-015-0483-8. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25840774
-
Role of MCP-1 in cardiovascular disease: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications.Clin Sci (Lond). 2009 Jul 2;117(3):95-109. doi: 10.1042/CS20080581. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19566488 Review.
-
Inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/CCR2 pathway.Circ Res. 2012 Jan 6;110(1):174-89. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243212. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22223213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MCPIP1 negatively regulates toll-like receptor 4 signaling and protects mice from LPS-induced septic shock.Cell Signal. 2013 May;25(5):1228-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.02.009. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23422584 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) regulates macrophage cytotoxicity in abdominal aortic aneurysm.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 14;9(3):e92053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092053. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24632850 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors STAT6 and KLF4 implement macrophage polarization via the dual catalytic powers of MCPIP.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 15;194(12):6011-23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402797. Epub 2015 May 1. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25934862 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and IL-1 activate translation of overlapping sets of mRNAs, including that of the negative regulator of inflammation, MCPIP1.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 28;288(26):19250-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.452649. Epub 2013 May 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23658019 Free PMC article.
-
A novel intracellular isoform of matrix metalloproteinase-2 induced by oxidative stress activates innate immunity.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034177. Epub 2012 Apr 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22509276 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

