Assessment of analytical reproducibility of 1H NMR spectroscopy based metabonomics for large-scale epidemiological research: the INTERMAP Study
- PMID: 16579598
- PMCID: PMC6561113
- DOI: 10.1021/ac0517085
Assessment of analytical reproducibility of 1H NMR spectroscopy based metabonomics for large-scale epidemiological research: the INTERMAP Study
Abstract
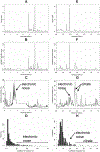
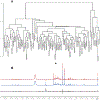
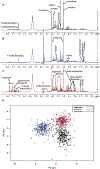
Large-scale population phenotyping for molecular epidemiological studies is subject to all the usual criteria of analytical chemistry. As part of a major phenotyping investigation we have used high-resolution 1H NMR spectroscopy to characterize 24-h urine specimens obtained from population samples in Aito Town, Japan (n = 259), Chicago, IL (n = 315), and Guangxi, China (n = 278). We have investigated analytical reproducibility, urine specimen storage procedures, interinstrument variability, and split specimen detection. Our data show that the multivariate analytical reproducibility of the NMR screening platform was >98% and that most classification errors were due to urine specimen handling inhomogeneity. Differences in metabolite profiles were then assessed for Aito Town, Chicago, and Guangxi population samples; novel combinations of biomarkers were detected that separated the population samples. These cross-population differences in urinary metabolites could be related to genetic, dietary, and gut microbial factors.
Figures
References
-
- Nicholson JK; Lindon JC; Holmes E Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson JK; Connelly J; Lindon JC; Holmes E Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2002, 1, 153–161. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson JK; Wilson ID Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2003, 2, 668–676. - PubMed
-
- Griffin JL; Williams HJ; Sang E; Clarke K; Rae C; Nicholson JK Anal. Biochem 2001, 293, 16–21. - PubMed
-
- Holmes E; Caddick S; Lindon JC; Wilson ID; Kryvawych S; Nicholson JK Biochem. Pharmacol 1995, 49, 1349–1359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

