Type specific seroprevalence of HSV-1 and HSV-2 in four geographical regions of Poland
- PMID: 16581747
- PMCID: PMC2564693
- DOI: 10.1136/sti.2005.015446
Type specific seroprevalence of HSV-1 and HSV-2 in four geographical regions of Poland
Abstract
Objective: To examine the type specific seroprevalence of herpes simplex virus (HSV) types 1 and 2 infections, stratified by age and gender, and associated risk factors for HSV-2 seropositivity in Poland.
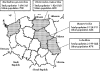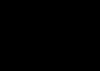
Methods: 2257 serum samples of individuals from 15-65 years were randomly selected from serum banks in four different geographical regions of Poland, including the Zachodnio-pomorskie, Warmińsko-mazurskie, Lubelskie, and Mazowieckie districts. Type specific serum antibodies to HSV-1 and HSV-2 were detected using HerpeSelect IgG ELISA tests.
Results: Overall prevalences of type specific HSV-1 and HSV-2 serum antibodies were 90.4% and 9.3%, respectively. Age standardised HSV-2 seroprevalence was higher in women (9.7%) than men (8.8%) (p = 0.06), and increased notably with age from 4% in 15-24 year olds to 12% in those aged 50-65 years. HSV-1 seroprevalence was consistently higher than HSV-2 seroprevalence in each specific age group, ranging from 74.5% in 15-24 year olds to 98.8% in 50-65 year olds. HSV-2 seroprevalence varied significantly by geographical region, with the highest prevalence in the Zachodnio-pomorskie district (12%). Significant multivariate risk factors for HSV-2 seropositivity included older age, female gender, and geographical place of residence.
Conclusion: This large survey found a notably high seroprevalence of HSV-1, even among young female adolescents 15-19 years of age (80%). HSV-2 seropositivity was under 12% in all age groups surveyed in Poland, tending to be among the lowest overall HSV-2 seropositivity rates reported thus far in Europe.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JMP is a full time employee of GSK. All other others have no competing interests to declare.
References
-
- Whitley R, Kimberlin D W, Roizman B. Herpes simplex viruses. Clin Infect Dis 199826541–555. - PubMed
-
- Roizman B, Sears A E. Herpes simplex viruses and their replication. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, eds. Fields virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott‐Raven, 1996
-
- Aurelian L. Herpes simplex viruses (Herpesviridae). General features. In, Granoff A, Webster RG, eds. Encyclopedia of virology London, Academic Press 1999
-
- Kinghorn G R. Herpes simplex type 1 genital infections. Herpes 199964–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical