Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus papain-like protease: structure of a viral deubiquitinating enzyme
- PMID: 16581910
- PMCID: PMC1458639
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510851103
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus papain-like protease: structure of a viral deubiquitinating enzyme
Abstract
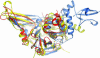
Replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus (SARS-CoV) requires proteolytic processing of the replicase polyprotein by two viral cysteine proteases, a chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro) and a papain-like protease (PLpro). These proteases are important targets for development of antiviral drugs that would inhibit viral replication and reduce mortality associated with outbreaks of SARS-CoV. In this work, we describe the 1.85-A crystal structure of the catalytic core of SARS-CoV PLpro and show that the overall architecture adopts a fold closely resembling that of known deubiquitinating enzymes. Key features, however, distinguish PLpro from characterized deubiquitinating enzymes, including an intact zinc-binding motif, an unobstructed catalytically competent active site, and the presence of an intriguing, ubiquitin-like N-terminal domain. To gain insight into the active-site recognition of the C-terminal tail of ubiquitin and the related LXGG motif, we propose a model of PLpro in complex with ubiquitin-aldehyde that reveals well defined sites within the catalytic cleft that help to account for strict substrate-recognition motifs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
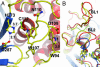

References
-
- Rota P. A., Oberste M. S., Monroe S. S., Nix W. A., Campagnoli R., Icenogle J. P., Penaranda S., Bankamp B., Maher K., Chen M. H., et al. Science. 2003;300:1394–1399. - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek T. G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C. S., Zaki S. R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J. A., Lim W., et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Thiel V., Ivanov K. A., Putics A., Hertzig T., Schelle B., Bayer S., Weissbrich B., Snijder E. J., Rabenau H., Doerr H. W., et al. J. Gen. Virol. 2003;84:2305–2315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

