Locus-specific control of DNA methylation by the Arabidopsis SUVH5 histone methyltransferase
- PMID: 16582009
- PMCID: PMC1456864
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.041400
Locus-specific control of DNA methylation by the Arabidopsis SUVH5 histone methyltransferase
Abstract
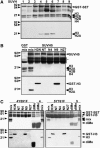
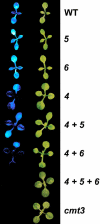
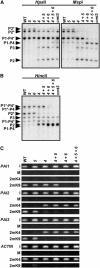
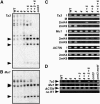
In Arabidopsis thaliana, heterochromatin formation is guided by double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), which triggers methylation of histone H3 at Lys-9 (H3 mK9) and CG plus non-CG methylation on identical DNA sequences. At heterochromatin targets including transposons and centromere repeats, H3 mK9 mediated by the Su(var)3-9 homologue 4 (SUVH4)/KYP histone methyltransferase (MTase) is required for the maintenance of non-CG methylation by the CMT3 DNA MTase. Here, we show that although SUVH4 is the major H3 K9 MTase, the SUVH5 protein also has histone MTase activity in vitro and contributes to the maintenance of H3 mK9 and CMT3-mediated non-CG methylation in vivo. Strikingly, the relative contributions of SUVH4, SUVH5, and a third related histone MTase, SUVH6, to non-CG methylation are locus-specific. For example, SUVH4 and SUVH5 together control transposon sequences with only a minor contribution from SUVH6, whereas SUVH4 and SUVH6 together control a transcribed inverted repeat source of dsRNA with only a minor contribution from SUVH5. This locus-specific variation suggests different mechanisms for recruiting or activating SUVH enzymes at different heterochromatic sequences. The suvh4 suvh5 suvh6 triple mutant loses both monomethyl and dimethyl H3 K9 at target loci. The suvh4 suvh5 suvh6 mutant also displays a loss of non-CG methylation similar to a cmt3 mutant, indicating that SUVH4, SUVH5, and SUVH6 together control CMT3 activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
H3 lysine 9 methylation is maintained on a transcribed inverted repeat by combined action of SUVH6 and SUVH4 methyltransferases.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(23):10507-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10507-10515.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16287862 Free PMC article.
-
HISTONE DEACETYLASE6 Acts in Concert with Histone Methyltransferases SUVH4, SUVH5, and SUVH6 to Regulate Transposon Silencing.Plant Cell. 2017 Aug;29(8):1970-1983. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00570. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Plant Cell. 2017. PMID: 28778955 Free PMC article.
-
Control of CpNpG DNA methylation by the KRYPTONITE histone H3 methyltransferase.Nature. 2002 Apr 4;416(6880):556-60. doi: 10.1038/nature731. Epub 2002 Mar 17. Nature. 2002. PMID: 11898023
-
Heterochromatin proteins and the control of heterochromatic gene silencing in Arabidopsis.J Plant Physiol. 2006 Feb;163(3):358-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2005.10.015. Epub 2005 Dec 27. J Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16384625 Review.
-
Chromatin-based silencing mechanisms.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004 Oct;7(5):521-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.07.003. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004. PMID: 15337094 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic and co-expression analysis of OsSET gene family in rice.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 7;8(6):e65426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065426. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762371 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic switches of tobacco transgenes associate with transient redistribution of histone marks in callus culture.Epigenetics. 2013 Jun;8(6):666-76. doi: 10.4161/epi.24613. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23770973 Free PMC article.
-
Developmentally non-redundant SET domain proteins SUVH2 and SUVH9 are required for transcriptional gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Aug;79(6):623-33. doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9934-x. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22669745 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of a Jumonji-C domain-containing histone demethylase in DRM2-mediated maintenance of DNA methylation.EMBO Rep. 2010 Dec;11(12):950-5. doi: 10.1038/embor.2010.158. Epub 2010 Nov 5. EMBO Rep. 2010. PMID: 21052090 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of plant immunity: from chromatin codes to plant disease resistance.aBIOTECH. 2023 Mar 17;4(2):124-139. doi: 10.1007/s42994-023-00101-z. eCollection 2023 Jun. aBIOTECH. 2023. PMID: 37581024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Baumbusch, L.O., Thorstensen, T., Krauss, V., Fischer, A., Naumann, K., Assalkhou, R., Schulz, I., Reuter, G., and Aalen, R.B. (2001). The Arabidopsis thaliana genome contains at least 29 active genes encoding SET domain proteins that can be assigned to four evolutionarily conserved classes. Nucleic Acids Res. 29 4319–4333. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

