Method of predicting splice sites based on signal interactions
- PMID: 16584568
- PMCID: PMC1526722
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6150-1-10
Method of predicting splice sites based on signal interactions
Abstract
Background: Predicting and proper ranking of canonical splice sites (SSs) is a challenging problem in bioinformatics and machine learning communities. Any progress in SSs recognition will lead to better understanding of splicing mechanism. We introduce several new approaches of combining a priori knowledge for improved SS detection. First, we design our new Bayesian SS sensor based on oligonucleotide counting. To further enhance prediction quality, we applied our new de novo motif detection tool MHMMotif to intronic ends and exons. We combine elements found with sensor information using Naive Bayesian Network, as implemented in our new tool SpliceScan.
Results: According to our tests, the Bayesian sensor outperforms the contemporary Maximum Entropy sensor for 5' SS detection. We report a number of putative Exonic (ESE) and Intronic (ISE) Splicing Enhancers found by MHMMotif tool. T-test statistics on mouse/rat intronic alignments indicates, that detected elements are on average more conserved as compared to other oligos, which supports our assumption of their functional importance. The tool has been shown to outperform the SpliceView, GeneSplicer, NNSplice, Genio and NetUTR tools for the test set of human genes. SpliceScan outperforms all contemporary ab initio gene structural prediction tools on the set of 5' UTR gene fragments.
Conclusion: Designed methods have many attractive properties, compared to existing approaches. Bayesian sensor, MHMMotif program and SpliceScan tools are freely available on our web site.
Reviewers: This article was reviewed by Manyuan Long, Arcady Mushegian and Mikhail Gelfand.
Figures

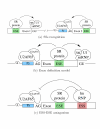




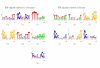




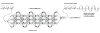
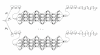
 .
.


References
-
- Krogh A. Gene finding: putting the parts together. In: Bishop MJ, editor. Guide to Human Genome Computing. 2. Academic Press, San Diego, CA; 1998. pp. 261–274.
-
- Burge C, Karlin S. Predictions of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1997;268:78–94. - PubMed
-
- Krogh A. Two methods for improving performance of an HMM and their application for gene-finding. In: Gaasterland T et al, editor. Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. AAAI Press, Menlo Park, CA; 1997. pp. 179–186. - PubMed
-
- Rogozin I, Milanesi L. Analysis of Donor Splice Sites in Different Eukaryotic Organisms. Journal of Molecular Evolution. 1997;45:50–59. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

