A set of highly informative rat simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) markers and genetically defined rat strains
- PMID: 16584579
- PMCID: PMC1475628
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-7-19
A set of highly informative rat simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) markers and genetically defined rat strains
Abstract
Background: The National Bio Resource Project for the Rat in Japan (NBRP-Rat) is focusing on collecting, preserving and distributing various rat strains, including spontaneous mutant, transgenic, congenic, and recombinant inbred (RI) strains. To evaluate their value as models of human diseases, we are characterizing them using 109 phenotypic parameters, such as clinical measurements, internal anatomy, metabolic parameters, and behavioral tests, as part of the Rat Phenome Project. Here, we report on a set of 357 simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) markers and 122 rat strains, which were genotyped by the marker set.
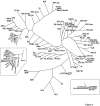
Results: The SSLP markers were selected according to their distribution patterns throughout the whole rat genome with an average spacing of 7.59 Mb. The average number of informative markers between all possible pairs of strains was 259 (72.5% of 357 markers), showing their high degree of polymorphism. From the genetic profile of these rat inbred strains, we constructed a rat family tree to clarify their genetic background.
Conclusion: These highly informative SSLP markers as well as genetically and phenotypically defined rat strains are useful for designing experiments for quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and to choose strategies for developing new genetic resources. The data and resources are freely available at the NBRP-Rat web site 1.
Figures



References
-
- National Bio Resource Project for the Rat in Japan http://www.anim.med.kyoto-u.ac.jp/NBR
-
- Kwitek AE, Gullings-Handley J, Yu J, Carlos DC, Orlebeke K, Nie J, Eckert J, Lemke A, Andrae JW, Bromberg S, et al. High-density rat radiation hybrid maps containing over 24,000 SSLPs, genes, and ESTs provide a direct link to the rat genome sequence. Genome Res. 2004;14:750–757. doi: 10.1101/gr.1968704. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

