Anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus immune responses: the role played by V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells
- PMID: 16586361
- PMCID: PMC7110256
- DOI: 10.1086/502975
Anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus immune responses: the role played by V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells
Erratum in
- J Infect Dis. 2006 Jul 15;194(2):267
Abstract
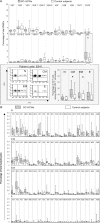
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV) strain. Analyses of T cell repertoires in health care workers who survived SARS-CoV infection during the 2003 outbreak revealed that their effector memory V gamma 9V delta 2 T cell populations were selectively expanded ~3 months after the onset of disease. No such expansion of their alpha beta T cell pools was detected. The expansion of the V gamma 9V delta 2 T cell population was associated with higher anti-SARS-CoV immunoglobulin G titers. In addition, in vitro experiments demonstrated that stimulated V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells display an interferon- gamma -dependent anti-SARS-CoV activity and are able to directly kill SARS-CoV-infected target cells. These findings are compatible with the possibility that V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells play a protective role during SARS.
Figures

References
-
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–66. - PubMed
-
- Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, et al. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1986–94. - PubMed
-
- Gioia C, Horejsh D, Agrati C, et al. T-cell response profiling to biological threat agents including the SARS coronavirus. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2005;18:525–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

