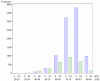
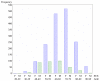
Patients with femoral or distal forearm fracture in Germany: a prospective observational study on health care situation and outcome
- PMID: 16594996
- PMCID: PMC1526725
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-6-87
Patients with femoral or distal forearm fracture in Germany: a prospective observational study on health care situation and outcome
Abstract
Background: Distal radius and proximal femoral fractures are typical injuries in later life, predominantly due to simple falls, but modulated by other relevant factors such as osteoporosis. Fracture incidence rates rise with age. Because of the growing proportion of elderly people in Western industrialized societies, the number of these fractures can be expected to increase further in the coming years, and with it the burden on healthcare resources. Our study therefore assessed the effects of these injuries on the health status of older people over time. The purpose of this paper is to describe the study method, clinical parameters of fracture patients during hospitalization, mortality up to one and a half years after discharge in relation to various factors such as type of fracture, and to describe changes in mobility and living situation.
Methods: Data were collected from all consecutive patients (no age limit) admitted to 423 hospitals throughout Germany with distal radius or femoral fractures (57% acute-care, femoral and forearm fractures; 43% rehabilitation, femoral fractures only) between January 2002 and September 2003. Polytrauma and coma patients were excluded. Demographic characteristics, exact fracture location, mobility and living situation, clinical and laboratory parameters were examined. Current health status was assessed in telephone interviews conducted on average 6-7 months after discharge. Where telephone contact could not be established, at least survival status (living/deceased/date of death) was determined.
Results: The study population consisted of 12,520 femoral fracture patients (86.8% hip fractures), average age 77.5 years, 76.5% female, and 2,031 forearm fracture patients, average age 67.6 years, 81.6% female. Women's average age was 6.6 (femoral fracture) to 10 years (forearm fracture) older than men's (p < 0.0001). Only 4.6% of femoral fracture patients experienced changes in their living situation post-discharge (53% because of the fracture event), although less than half of subjects who were able to walk without assistive devices prior to the fracture event (76.7%) could still do so at time of interview (34.9%). At time of interview, 1.5% of subjects were bed-ridden (0.2% before fracture). Forearm fracture patients reported no change in living situation at all. Of the femoral fracture patients 119 (0.95%), and of the forearm fracture patients 3 (0.15%) died during hospital stay. Post-discharge (follow-up one and a half years) 1,463 femoral fracture patients died (19.2% acute-care patients, 8.5% rehabilitation patients), but only 60 forearm fracture patients (3.0%). Ninety percent of femoral fracture deaths happened within the first year, approximately 66% within the first 6 months. More acute-care patients with a pertrochanteric fracture died within one year post-discharge (20.6%) than patients with a cervical fracture (16.1%).
Conclusion: Mortality after proximal femoral fracture is still alarmingly high and highest after pertrochanteric fracture. Although at time of interview more than half of femoral fracture patients reported reduced mobility, most patients (96%) attempt to live at home. Since forearm fracture patients were on average 10 years younger than femoral fracture patients, forearm fractures may be a means of diagnosing an increased risk of later hip fractures.
Figures
References
-
- Schwartz AV, Kelsey JL, Maggi S, Tuttleman M, Ho SC, Jonsson PV, Poor G, Sisson de Castro JA, Xu L, Matkin CC, Nelson LM, Heyse SP. International variation in the incidence of hip fractures: cross-national project on osteoporosis for the World Health Organization Program for Research on Aging. Osteoporos Int. 1999;9:242–253. doi: 10.1007/s001980050144. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical