Effects of abciximab on key pattern of human coronary restenosis in vitro: impact of the SI/MPL-ratio
- PMID: 16595000
- PMCID: PMC1475639
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-6-14
Effects of abciximab on key pattern of human coronary restenosis in vitro: impact of the SI/MPL-ratio
Abstract
Background: The significant reduction of angiographic restenosis rates in the ISAR-SWEET study (intracoronary stenting and antithrombotic regimen: is abciximab a superior way to eliminate elevated thrombotic risk in diabetes) raises the question of whether abciximab acts on clopidogrel-independent mechanisms in suppressing neointimal hyperplasia. The current study investigates the direct effect of abciximab on ICAM-1 expression, migration and proliferation.
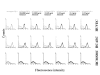
Methods: ICAM-1: Part I of the study investigates in cytoflow studies the effect of abciximab (0.0002, 0.002, 0.02, 0.2, 2.0, and 20.0 microg/ml) on TNF-alpha induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). Migration: Part II of the study explored the effect of abciximab (0.0002, 0.002, 0.02, 0.2, 2.0, and 20.0 microg/ml) on migration of HCMSMC over a period of 24 h. Proliferation: Part III of the study investigated the effect of abciximab (0.0002, 0.002, 0.02, 0.2, 2.0, and 20.0 microg/ml) on proliferation of HUVEC, HCAEC, and HCMSMC after an incubation period of 5 days.
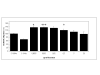
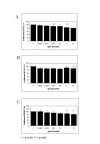
Results: ICAM-1: In human venous endothelial cells (HUVEC), human coronary endothelial cells (HCAEC) and human coronary medial smooth muscle cells (HCMSMC) no inhibitory or stimulatory effect on expression of ICAM-1 was detected. Migration: After incubation of HCMSMC with abciximab in concentrations of 0.0002-2 microg/ml a stimulatory effect on cell migration was detected, statistical significance was achieved after incubation with 0.002 microg/ml (p < 0.05), 0.002 microg/ml (p < 0.001), and 0.2 microg/ml (p < 0.05). Proliferation: Small but statistically significant antiproliferative effects of abciximab were detected after incubation of HUVEC (0.02 and 2.0 microg/ml; p = 0.01 and p < 0.01), HCAEC (2.0 and 20.0 microg/ml; p < 0.05 and p < 0,01), and HCMSMC (2.0 and 20.0 microg/ml; p < 0.05 and p < 0.05). The significant inhibition (SI) of cell proliferation found in HCAEC and HCMSMC was achieved with drug concentrations more than 10 times beyond the maximal plasma level (MPL), resulting in a SI/MPL-ratio > 1.
Conclusion: Thus, the anti-restenotic effects of systemically administered abciximab reported in the ISAR-SWEET-study were not caused by a direct inhibitory effect on ICAM-1 expression, migration or proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sirolimus inhibits key events of restenosis in vitro/ex vivo: evaluation of the clinical relevance of the data by SI/MPL- and SI/DES-ratios.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2007 May 11;7:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-7-15. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2007. PMID: 17498286 Free PMC article.
-
Valproic acid inhibits proliferation of human coronary vascular cells (SI/MPL-ratio: 0.5): a novel candidate for systemic and local therapy of postinterventional restenosis.Coron Artery Dis. 2010 Aug;21(5):286-91. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e3283349cd7. Coron Artery Dis. 2010. PMID: 20508518
-
Direct inhibitory effects of Ganciclovir on ICAM-1 expression and proliferation in human coronary vascular cells (SI/MPL-ratio: >1).Med Sci Monit. 2011 Jan;17(1):PI1-6. doi: 10.12659/msm.881310. Med Sci Monit. 2011. PMID: 21169918 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mycophenolate mofetil on key pattern of coronary restenosis: a cascade of in vitro and ex vivo models.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2005 May 12;5(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-5-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2005. PMID: 15890069 Free PMC article.
-
ICAM-1 signaling in endothelial cells.Pharmacol Rep. 2009 Jan-Feb;61(1):22-32. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(09)70004-0. Pharmacol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19307690 Review.
Cited by
-
Sirolimus inhibits key events of restenosis in vitro/ex vivo: evaluation of the clinical relevance of the data by SI/MPL- and SI/DES-ratios.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2007 May 11;7:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-7-15. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2007. PMID: 17498286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mehilli J, Kastrati A, Schuhlen H, Dibra A, Dotzer F, von Beckerath N, Bollwein H, Pache J, Dirschinger J, Berger PP, Schömig A. Intracoronary stenting and antithrombotic regimen: Is abciximab a superior way to eliminate elevated thrombotic risk in diabetes (ISAR-SWEET) study Investigators. Circulation. 2004;14:3627–3635. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000148956.93631.4D. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lincoff AM, Califf RM, Anderson KM, Weisman HF, Aguirre FV, Kleimann NS, Harrington RA, Topol EJ. Evidence for prevention of death and myocardial infarction with platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blockade by abciximab (c7E3 Fab) among patients with unstable angina undergoing percutaneous coronary revascularization. EPIC Investigators. Evaluation of 7E3 in preventing ischemic complications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997;30:149–156. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(97)00110-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kleiman NS, Lincoff AM, Kereiakes DJ, Miller DP, Aguirre FV, Anderson KM, Weisman HF, Califf RM, Topol EJ. Diabetes mellitus, glycoprotein Iib/IIIa blockade, and heparin: evidence for a complex interaction in a multicenter trial. EPILOG investigators. Circulation. 1998;97:1912–1920. - PubMed
-
- Marso SP, Lincoff AM, Ellis SG, Bhatt DL, Tanguay JF, Kleiman NS, Hammoud T, Booth JE, Sapp SK, Topol EJ. Optimizing the percutaneous interventional outcomes for patients with diabetes mellitus: results of the EPISTENT (Evaluation of platelet IIb/IIIa inhibitor for stenting trial) diabetes substudy. Circulation. 1999;100:2477–2484. - PubMed
-
- Lincoff AM, Califf RM, Moliterno DJ, Ellis SG, Ducas J, Kramer JH, Kleiman NS, Cohen EA, Booth JE, Sapp SK, Cabot CF, Topol EJ. Complementary clinical benefits of coronary-artery stenting and blockade of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors. Evaluation of platelet IIb/IIIa inhibition in stenting investigators. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:319–327. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199907293410503. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

