Effect of nurse-directed hypertension treatment among First Nations people with existing hypertension and diabetes mellitus: the Diabetes Risk Evaluation and Microalbuminuria (DREAM 3) randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 16595786
- PMCID: PMC1435956
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.050030
Effect of nurse-directed hypertension treatment among First Nations people with existing hypertension and diabetes mellitus: the Diabetes Risk Evaluation and Microalbuminuria (DREAM 3) randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: First Nations people with diabetes mellitus and hypertension are at greater risk of renal and cardiovascular complications than are non-native patients because of barriers to health care services. We conducted this randomized controlled trial to assess whether a community-based treatment strategy implemented by home care nurses would be effective in controlling hypertension in First Nations people with existing hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
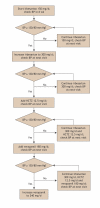
Methods: We compared 2 community-based strategies for controlling hypertension in First Nations people with existing hypertension and diabetes. In the intervention group, a home care nurse followed a predefined treatment algorithm of pharmacologic antihypertensive therapy. In the control group, treatment decisions were made by each subject's primary care physician. The primary outcome measure was the difference between the 2 groups in the change in systolic blood pressure after 12 months. Secondary outcome measures were the change in diastolic blood pressure over time, the change in urine albumin status and the incidence of adverse events.
Results: Both groups experienced a significant reduction in systolic blood pressure by the final visit (by 24.0 [standard deviation (SD) 13.5] mm Hg in the intervention group and by 17.0 [SD 18.6] mm Hg in the control group); p < 0.001 in each case). However, the difference between the 2 groups in this change was not significant. Patients in the intervention group had a larger decrease in diastolic blood pressure over time than did those in the control group (by 11.6 [SD 10.6] mm Hg v. 6.8 [SD 11.1] mm Hg respectively; p = 0.05). The groups did not differ significantly in terms of changes in urine albumin excretion or incidence of adverse events.
Interpretation: High rates of blood pressure control in the community were achieved in both groups in the DREAM 3 study. The addition of a home care nurse to implement a treatment strategy for blood pressure control was more effective in lowering diastolic than systolic blood pressure compared with home care visits for blood pressure monitoring alone and follow-up treatment by a family physician.
Figures

Comment in
-
The quest to improve Aboriginal health.CMAJ. 2006 Apr 25;174(9):1233, 1237. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.060379. CMAJ. 2006. PMID: 16636314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Overcoming clinical inertia in the management of hypertension.CMAJ. 2006 Apr 25;174(9):1285-6. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.060243. CMAJ. 2006. PMID: 16636328 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jones CA, Francis ME, Eberhardt MS, et al. Microalbuminuria in the US population: third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis 2002;39:445-59. - PubMed
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial. Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) [published erratum appears in JAMA 2003;289(2):178]. JAMA 2002;288: 2981-97. - PubMed
-
- Artinian NT, Washington OG, Templin TN. Effects of home telemonitoring and community-based monitoring on blood pressure control in urban African Americans: a pilot study. Heart Lung 2001;30:191-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
