Effects of reinforcement schedule on facilitation of operant extinction by chlordiazepoxide
- PMID: 16596968
- PMCID: PMC1389770
- DOI: 10.1901/jeab.2005.71-04
Effects of reinforcement schedule on facilitation of operant extinction by chlordiazepoxide
Abstract
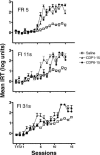
Learning and memory are central topics in behavioral neuroscience, and inbred mice strains are widely investigated. However, operant conditioning techniques are not as extensively used in this field as they should be, given the effectiveness of the methodology of the experimental analysis of behavior. In the present study, male C57B1/6 mice, widely used as background for transgenic studies, were trained to lever press on discrete-trial fixed-ratio 5 or fixed-interval (11 s or 31 s) schedules of food reinforcement and then exposed to 15 extinction sessions following vehicle or chlordiazepoxide injections (15 mg/kg i.p., administered either prior to all extinction sessions, or prior to the final 10 extinction sessions). Extinction of operant behavior was facilitated by drug administration following training on either schedule, but this facilitation only occurred once a number of extinction sessions had taken place. The extinction process proceeded more rapidly following fixed-interval training. Resistance to extinction was equally high following training with either schedule type, and was reduced by drug administration in both cases. These phenomena were evident in individual cumulative records and in analyses of group data. Results are interpreted in terms of phenomena of operant extinction identified in Skinner's (1938) Behavior of Organisms, and by behavioral momentum theory. These procedures could be used to extend the contribution of operant conditioning to contemporary behavioral neuroscience.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Facilitation of extinction of operant behaviour in C57Bl/6 mice by chlordiazepoxide and D-cycloserine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Sep;223(2):223-35. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2710-4. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22526539
-
Effects of chlordiazepoxide on extinction and re-acquisition of operant behaviour in mice.Behav Pharmacol. 2004 May;15(3):225-32. Behav Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15187580
-
Facilitation of extinction and re-extinction of operant behavior in mice by chlordiazepoxide and D-cycloserine.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013 May;102:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013. PMID: 23416058
-
Effects of drugs that potentiate GABA on extinction of positively-reinforced operant behaviour.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004 May;28(3):229-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2004.01.003. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004. PMID: 15225968 Review.
-
Aggression induced by intermittent positive reinforcement.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1982 Spring;6(1):15-37. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(82)90004-5. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1982. PMID: 6280117 Review.
Cited by
-
Response inhibition is impaired by developmental methylmercury exposure: acquisition of low-rate lever-pressing.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Sep 15;253:196-205. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.05.038. Epub 2013 May 27. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23721962 Free PMC article.
-
Facets of Pavlovian and operant extinction.Behav Processes. 2012 May;90(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2012.03.009. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Behav Processes. 2012. PMID: 22465468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin differentially modulates pavlovian cue and context fear acquisition.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017 Jun 1;12(6):976-983. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsx028. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28402515 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vivo effects of abused 'bath salt' constituent 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in mice: drug discrimination, thermoregulation, and locomotor activity.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Mar;38(4):563-73. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.233. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23212455 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitation of extinction of operant behaviour in C57Bl/6 mice by chlordiazepoxide and D-cycloserine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Sep;223(2):223-35. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2710-4. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22526539
References
-
- Davidson T.L, Jerrard L.E. The hippocampus and inhibitory learning: A ‘Gray’ area? Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 2004;28:261–271. - PubMed
-
- Davis M, Walker D.L, Myers K.M. Role of the amygdala in fear extinction measured with potentiated startle. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2003;985:218–232. - PubMed
-
- Fantino E. Conditioned reinforcement: Choice and information. In: Honig W.K, Staddon J.E.R, editors. Handbook of operant behavior. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall; 1977. pp. 313–339.
-
- Ferster C.B, Skinner B.F. Schedules of reinforcement. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts; 1957.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

