Fumarate hydratase enzyme activity in lymphoblastoid cells and fibroblasts of individuals in families with hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer
- PMID: 16597677
- PMCID: PMC2564577
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2006.041087
Fumarate hydratase enzyme activity in lymphoblastoid cells and fibroblasts of individuals in families with hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer
Abstract
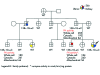
Background: Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC) is the autosomal dominant heritable syndrome with predisposition to development of renal cell carcinoma and smooth muscle tumours of the skin and uterus.
Objective: To measure the fumarate hydratase (FH) enzyme activity in lymphoblastoid cell lines and fibroblast cell lines of individuals with HLRCC and other familial renal cancer syndromes.
Methods: FH enzyme activity was determined in the whole cell, cytosolic, and mitochondrial fractions in 50 lymphoblastoid and 16 fibroblast cell lines including cell lines from individuals with HLRCC with 16 different mutations.
Results: Lymphoblastoid cell lines (n = 20) and fibroblast cell lines (n = 11) from individuals with HLRCC had lower FH enzyme activity than cells from normal controls (p<0.05). The enzyme activity in lymphoblastoid cell lines from three individuals with mutations in R190 was not significantly different from individuals with other missense mutations. The cytosolic and mitochondrial FH activity of cell lines from individuals with HLRCC was reduced compared with those from control cell lines (p<0.05). There was no significant difference in enzyme activity between control cell lines (n = 4) and cell lines from affected individuals with other hereditary renal cancer syndromes (n = 22).
Conclusions: FH enzyme activity testing provides a useful diagnostic method for confirmation of clinical diagnosis and screening of at-risk family members.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none declared.
Similar articles
-
Missense mutations in fumarate hydratase in multiple cutaneous and uterine leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer.J Mol Diagn. 2005 Oct;7(4):437-43. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60574-0. J Mol Diagn. 2005. PMID: 16237213 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Detection of Germline Mutation of Fumarate Hydratase in Women With Uterine Smooth Muscle Tumors Using Pathology-based Screening to Trigger Genetic Counseling for Hereditary Leiomyomatosis Renal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome: A 5-Year Single Institutional Experience.Am J Surg Pathol. 2019 May;43(5):639-655. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001222. Am J Surg Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30741757
-
Genetic and functional analyses of FH mutations in multiple cutaneous and uterine leiomyomatosis, hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cancer, and fumarate hydratase deficiency.Hum Mol Genet. 2003 Jun 1;12(11):1241-52. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg148. Hum Mol Genet. 2003. PMID: 12761039
-
Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma: Morphological appraisal with a comprehensive review of differential diagnoses.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2020 Feb;63(Supplement):S7-S17. doi: 10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_877_19. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32108620 Review.
-
Mechanisms of disease: hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer--a distinct form of hereditary kidney cancer.Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2007 Feb;4(2):104-10. doi: 10.1038/ncpuro0711. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2007. PMID: 17287871 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic counseling in renal masses.Adv Urol. 2008;2008:720840. doi: 10.1155/2008/720840. Epub 2008 Nov 9. Adv Urol. 2008. PMID: 19009041 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple hits for the association of uterine fibroids on human chromosome 1q43.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058399. Epub 2013 Mar 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555580 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genetic predisposition to kidney cancer.Semin Oncol. 2016 Oct;43(5):566-574. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Semin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27899189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No evidence for the role of somatic mutations and promoter hypermethylation of FH gene in the tumorigenesis of nonsyndromic uterine leiomyomas.Tumour Biol. 2012 Oct;33(5):1411-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0391-6. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Tumour Biol. 2012. PMID: 22528940
-
Uterine smooth muscle tumors with features suggesting fumarate hydratase aberration: detailed morphologic analysis and correlation with S-(2-succino)-cysteine immunohistochemistry.Mod Pathol. 2014 Jul;27(7):1020-7. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.215. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Mod Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24309325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tomlinson I P, Alam N A, Rowan A J, Barclay E, Jaeger E E, Kelsell D, Leigh I, Gorman P, Lamlum H, Rahman S, Roylance R R, Olpin S, Bevan S, Barker K, Hearle N, Houlston R S, Kiuru M, Lehtonen R, Karhu A, Vilkki S, Laiho P, Eklund C, Vierimaa O, Aittomaki K, Hietala M, Sistonen P, Paetau A, Salovaara R, Herva R, Launonen V, Aaltonen L A, Multiple Leiomyoma Consortium Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer. Nat Genet 200230406–410. - PubMed
-
- Toro J R, Nickerson M L, Wei M H, Warren M B, Glenn G M, Turner M L, Stewart L, Duray P, Tourre O, Sharma N, Choyke P, Stratton P, Merino M, Walther M M, Linehan W M, Schmidt L S, Zbar B. Mutations in the fumarate hydratase gene cause hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer in families in North America. Am J Hum Genet 20037395–106. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wei M H, Toure O, Glenn G M, Pithukpakorn M, Neckers L, Stolle C, Choyke P, Grubb R, Middelton L, Turner M L, Walther M M, Merino M J, Zbar B, Linehan W M, Toro J R. Novel mutations in FH and expansion of the spectrum of phenotypes expressed in families with hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer. J Med Genet 20064318–27. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous