Secondary structure, orientation, and oligomerization of phospholemman, a cardiac transmembrane protein
- PMID: 16597826
- PMCID: PMC2242498
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.051899406
Secondary structure, orientation, and oligomerization of phospholemman, a cardiac transmembrane protein
Abstract
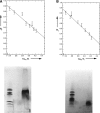
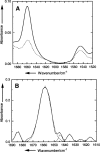
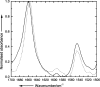
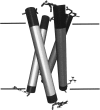
Human phospholemman (PLM) is a 72-residue protein, which is expressed at high density in the cardiac plasma membrane and in various other tissues. It forms ion channels selective for K+, Cl-, and taurine in lipid bilayers and colocalizes with the Na+/K+-ATPase and the Na+/Ca2+-exchanger, which may suggest a role in the regulation of cell volume. Here we present the first structural data based on synthetic peptides representing the transmembrane domain of PLM. Perfluoro-octaneoate-PAGE of reconstituted proteoliposomes containing PLM reveals a tetrameric homo-oligomerization. Infrared spectroscopy of proteoliposomes shows that the PLM peptide is completely alpha-helical, even beyond the hydrophobic core residues. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange experiments reveal that a core of 20-22 residues is not accessible to water, thus embedded in the lipid membrane. The maximum helix tilt is 17 degrees +/- 2 degrees obtained by attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy. Thus, our data support the idea of ion channel formation by the PLM transmembrane domain.
Figures
References
-
- Arkin I.T., MacKenzie K.R., Brünger A.T. 1997. Site-directed dichroism as a method for obtaining rotational and orientational constraints for orientated polymers J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119: 8973–8980.
-
- Byler D.M. and Susi H. 1986. Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra Biopolymers 25: 469–487. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z., Jones L.R., O'Brian J.J., Moorman J.R., Cala S.E. 1998. Structural domains in phospholemman: A possible role for the carboxyl terminus in channel inactivation Circ. Res. 82: 367–374. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z.H., Jones L.R., Moorman J.R. 1999. Ion currents through mutant phospholemman channel molecules Receptors Channels 6: 435–447. - PubMed
-
- Davis C.E., Patel M.K., Miller J.R., John J.E. III, Jones L.R., Tucker A.L., Mounsey J.P., Moorman J.R. 2004. Effects of phospholemman expression on swelling-activated ion currents and volume regulation in embryonic kidney cells Neurochem. Res. 29: 177–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

