Discovery of natural atypical nonhemolytic Listeria seeligeri isolates
- PMID: 16597942
- PMCID: PMC1449060
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2439-2448.2006
Discovery of natural atypical nonhemolytic Listeria seeligeri isolates
Abstract
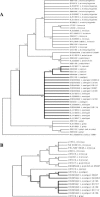
We found seven Listeria isolates, initially identified as isolates with the Xyl(+) Rha(-) biotype of Listeria welshimeri by phenotypic tests, which exhibited discrepant genotypic properties in a well-validated Listeria species identification oligonucleotide microarray. The microarray gives results of these seven isolates being atypical hly-negative L. seeligeri isolates, not L. welshimeri isolates. The aberrant L. seeligeri isolates were d-xylose fermentation positive, l-rhamnose fermentation negative (Xyl(+) Rha(-)), and nonhemolytic on blood agar and in the CAMP test with both Staphylococcus aureus (S(-) reaction) and Rhodococcus equi (R(-) reaction). All genes of the prfA cluster of L. seeligeri, located in the prs-ldh region, including the orfA2, orfD, prfA, orfE, plcA, hly, orfK, mpl, actA, dplcB, plcB, orfH, orfX, orfI, orfP, orfB, and orfA genes, were checked by PCR and direct sequencing for evidence of their presence in the atypical isolates. The prs-prfA cluster-ldh region of the L. seeligeri isolates was approximately threefold shorter due to the loss of orfD, prfA, orfE, plcA, hly, orfK, mpl, actA, dplcB, plcB, orfH, orfX, and orfI. The genetic map order of the cluster genes of all the atypical L. seeligeri isolates was prs-orfA2-orfP-orfB-orfA-ldh, which was comparable to the similar region in L. welshimeri, with the exception of the presence of orfA2. DNA sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of 17 housekeeping genes indicated an L. seeligeri genomic background in all seven of the atypical hly-negative L. seeligeri isolates. Thus, the novel biotype of Xyl(+) Rha(-) Hly(-) L. seeligeri strains can only be distinguished from Xyl(+) Rha(-) L. welshimeri strains genotypically, not phenotypically. In contrast, the Rha(+) Xyl(+) biotype of L. welshimeri would not present an identification issue.
Figures



References
-
- Aiyar, A. 2000. The use of CLUSTAL W and CLUSTAL X for multiple sequence alignment. Methods Mol. Biol. 132:221-241. - PubMed
-
- Allerberger, F. 2003. Listeria: growth, phenotypic differentiation and molecular microbiology. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 35:183-189. - PubMed
-
- Anisimova, M., J. P. Bielawski, and Z. Yang. 2001. Accuracy and power of the likelihood ratio test in detecting adaptive molecular evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 18:1585-1592. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

