Identification of essential operons with a rhamnose-inducible promoter in Burkholderia cenocepacia
- PMID: 16597956
- PMCID: PMC1448982
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2547-2555.2006
Identification of essential operons with a rhamnose-inducible promoter in Burkholderia cenocepacia
Abstract
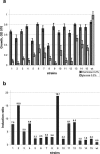
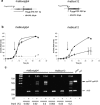
Scanning of bacterial genomes to identify essential genes is of biological interest, for understanding the basic functions required for life, and of practical interest, for the identification of novel targets for new antimicrobial therapies. In particular, the lack of efficacious antimicrobial treatments for infections caused by the Burkholderia cepacia complex is causing high morbidity and mortality of cystic fibrosis patients and of patients with nosocomial infections. Here, we present a method based on delivery of the tightly regulated rhamnose-inducible promoter P(rhaB) for identifying essential genes and operons in Burkholderia cenocepacia. We demonstrate that different levels of gene expression can be achieved by using two vectors that deliver P(rhaB) at two different distances from the site of insertion. One of these vectors places P(rhaB) at the site of transposon insertion, while the other incorporates the enhanced green fluorescent protein gene (e-gfp) downstream from P(rhaB). This system allows us to identify essential genes and operons in B. cenocepacia and provides a new tool for systematically identifying and functionally characterizing essential genes at the genomic level.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An expression vector containing a rhamnose-inducible promoter provides tightly regulated gene expression in Burkholderia cenocepacia.Plasmid. 2005 Nov;54(3):219-28. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2005.03.004. Epub 2005 May 31. Plasmid. 2005. PMID: 15925406
-
Genetic characterization of a multicomponent signal transduction system controlling the expression of cable pili in Burkholderia cenocepacia.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(12):3826-36. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3826-3836.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15175296 Free PMC article.
-
The Escherichia coli rhamnose promoter rhaP(BAD) is in Pseudomonas putida KT2440 independent of Crp-cAMP activation.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Feb;85(6):1923-33. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2245-8. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 19789867
-
Efflux pump genes of the resistance-nodulation-division family in Burkholderia cenocepacia genome.BMC Microbiol. 2006 Jul 20;6:66. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-6-66. BMC Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16857052 Free PMC article.
-
Burkholderia cenocepacia in cystic fibrosis: epidemiology and molecular mechanisms of virulence.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Jul;16(7):821-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03237.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 20880411 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Nonmevalonate Pathway in Burkholderia cenocepacia Increases Susceptibility to Certain β-Lactam Antibiotics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Apr 26;62(5):e02607-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02607-17. Print 2018 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29439968 Free PMC article.
-
A LysR-type transcriptional regulator in Burkholderia cenocepacia influences colony morphology and virulence.Infect Immun. 2008 Jan;76(1):38-47. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00874-07. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 17967860 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of O-Antigen and Hybrid Biosynthetic Locus in Burkholderia cenocepacia Clonal Variants Recovered from a Cystic Fibrosis Patient.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jun 8;8:1027. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01027. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28642745 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive Growth Enhances Conditional Growth Mutant Sensitivity to Antibiotics and Exposes a Two-Component System as an Emerging Antibacterial Target in Burkholderia cenocepacia.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Dec 27;61(1):e00790-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00790-16. Print 2017 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27799222 Free PMC article.
-
High confidence prediction of essential genes in Burkholderia cenocepacia.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040064. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bittner, M., S. Saldias, C. Estevez, M. Zaldivar, C. L. Marolda, M. A. Valvano, and I. Contreras. 2002. O-antigen expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi is regulated by nitrogen availability through RpoN-mediated transcriptional control of the rfaH gene. Microbiology 148:3789-3799. - PubMed
-
- Borukhov, S., O. Laptenko, and J. Lee. 2001. Escherichia coli transcript cleavage factors GreA and GreB: functions and mechanisms of action. Methods Enzymol. 342:64-76. - PubMed
-
- Cardona, S. T., and M. A. Valvano. 2005. An expression vector containing a rhamnose-inducible promoter provides tightly regulated gene expression in Burkholderia cenocepacia. Plasmid 54:219-228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

