Thiamine-auxotrophic mutants of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 are defective in cell-cell signaling and biocontrol factor expression
- PMID: 16597964
- PMCID: PMC1449068
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2606-2613.2006
Thiamine-auxotrophic mutants of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 are defective in cell-cell signaling and biocontrol factor expression
Abstract
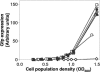
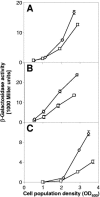
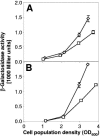
In the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0, the Gac/Rsm signal transduction pathway positively controls the synthesis of antifungal secondary metabolites and exoenzymes. In this way, the GacS/GacA two-component system determines the expression of three small regulatory RNAs (RsmX, RsmY, and RsmZ) in a process activated by the strain's own signal molecules, which are not related to N-acyl-homoserine lactones. Transposon Tn5 was used to isolate P. fluorescens CHA0 insertion mutants that expressed an rsmZ-gfp fusion at reduced levels. Five of these mutants were gacS negative, and in them the gacS mutation could be complemented for exoproduct and signal synthesis by the gacS wild-type allele. Furthermore, two thiamine-auxotrophic (thiC) mutants that exhibited decreased signal synthesis in the presence of 5 x 10(-8) M thiamine were found. Under these conditions, a thiC mutant grew normally but showed reduced expression of the three small RNAs, the exoprotease AprA, and the antibiotic 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol. In a gnotobiotic system, a thiC mutant was impaired for biological control of Pythium ultimum on cress. Addition of excess exogenous thiamine restored all deficiencies of the mutant. Thus, thiamine appears to be an important factor in the expression of biological control by P. fluorescens.
Figures


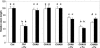
Similar articles
-
RsmY, a small regulatory RNA, is required in concert with RsmZ for GacA-dependent expression of biocontrol traits in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Nov;50(4):1361-79. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03774.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14622422
-
Three small RNAs jointly ensure secondary metabolism and biocontrol in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Nov 22;102(47):17136-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505673102. Epub 2005 Nov 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16286659 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory RNA as mediator in GacA/RsmA-dependent global control of exoproduct formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0.J Bacteriol. 2002 Feb;184(4):1046-56. doi: 10.1128/jb.184.4.1046-1056.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11807065 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction in plant-beneficial rhizobacteria with biocontrol properties.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002 Aug;81(1-4):385-95. doi: 10.1023/a:1020549019981. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002. PMID: 12448737 Review.
-
Small Regulatory RNAs of the Rsm Clan in Pseudomonas.Mol Microbiol. 2024 Oct;122(4):563-582. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15313. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Mol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39282792 Review.
Cited by
-
The Evanescent GacS Signal.Microorganisms. 2020 Nov 6;8(11):1746. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111746. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33172195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-species GacA-controlled induction of antibiosis in pseudomonads.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jan;73(2):650-4. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01681-06. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17098922 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics and Evolutionary Analysis of RNA-Binding Proteins of the CsrA Family in the Genus Pseudomonas.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Jul 10;7:127. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00127. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32754614 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA-dependent expression of secondary metabolism is controlled by Krebs cycle function in Pseudomonas fluorescens.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 11;284(50):34976-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.052571. Epub 2009 Oct 19. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19840935 Free PMC article.
-
Thiamine-Mediated Microbial Interaction between Auxotrophic Rhodococcus ruber ZM07 and Prototrophic Cooperators in the Tetrahydrofuran-Degrading Microbial Community H-1.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0454122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04541-22. Epub 2023 May 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37125924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao, Y., D. P. Lies, H. Fu, and G. P. Roberts. 1991. An improved Tn7-based system for the single-copy insertion of cloned genes into chromosomes of gram-negative bacteria. Gene 109:167-168. - PubMed
-
- Begley, T. P., D. M. Downs, S. E. Ealick, F. W. McLafferty, A. P. Van Loon, S. Taylor, N. Campobasso, H. J. Chiu, C. Kinsland, J. J. Reddick, and J. Xi. 1999. Thiamin biosynthesis in prokaryotes. Arch. Microbiol. 171:293-300. - PubMed
-
- Bonner, J. 1937. Vitamin B1, a growth factor for higher plants. Science 85:183-184. - PubMed
-
- Boulnois, G. J., J. M. Varley, G. S. Sharpe, and F. C. Franklin. 1985. Transposon donor plasmids, based on ColIb-P9, for use in Pseudomonas putida and a variety of other gram-negative bacteria. Mol. Gen. Genet. 200:65-67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

