ZXDC, a novel zinc finger protein that binds CIITA and activates MHC gene transcription
- PMID: 16600381
- PMCID: PMC1624858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.02.029
ZXDC, a novel zinc finger protein that binds CIITA and activates MHC gene transcription
Abstract
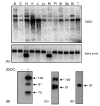
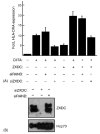
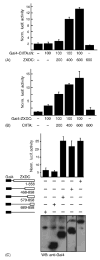
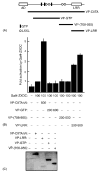
The class II trans-activator (CIITA) is recognized as the master regulator of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II gene transcription and contributes to the transcription of MHC class I genes. To better understand the function of CIITA, we performed yeast two-hybrid with the C-terminal 807 amino acids of CIITA, and cloned a novel human cDNA named zinc finger, X-linked, duplicated family member C (ZXDC). The 858 amino acid ZXDC protein contains 10 zinc fingers and a transcriptional activation domain, and was found to interact with the region of CIITA containing leucine-rich repeats. Over-expression of ZXDC in human cell lines resulted in super-activation of MHC class I and class II promoters by CIITA. Conversely, silencing of ZXDC expression reduced the ability of CIITA to activate transcription of MHC class II genes. Given the specific interaction between the ZXDC and CIITA proteins, as well as the effect of ZXDC on MHC gene transcription, it appears that ZXDC is an important regulator of both MHC class I and class II transcription.
Figures





References
-
- Boss JM, Jensen PE. Transcriptional regulation of the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Camacho-Carvajal MM, Klingler S, Schnappauf F, Hake SB, Steimle V. Importance of class II transactivator leucine-rich repeats for dominant-negative function and nucleo-cytoplasmic transport. Int Immunol. 2004;16:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Cress WD, Triezenberg SJ. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991;251:87–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

