Nicotine inhibits apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs by up-regulating XIAP and survivin
- PMID: 16601104
- PMCID: PMC1458878
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0509313103
Nicotine inhibits apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs by up-regulating XIAP and survivin
Abstract
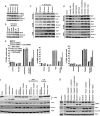
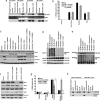
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) demonstrates a strong etiologic association with smoking. Although nicotine is not carcinogenic, it can induce cell proliferation and angiogenesis and suppress apoptosis induced by certain agents. Here we show that nicotine inhibits apoptosis induced by the drugs gemcitabine, cisplatin, and taxol, which are used to treat NSCLCs. This protection correlated with the induction of XIAP and survivin by nicotine in a panel of human NSCLC cell lines, and depletion of XIAP and survivin ablated the protective effects of nicotine. The antiapoptotic effects of nicotine were mediated by dihydro beta-erythroidine-sensitive alpha3-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and required the Akt pathway. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that nicotine stimulation caused an increased recruitment of E2F1 and concomitant dissociation of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (Rb) from survivin promoter in A549 cells. Moreover, ablation of E2F1 levels caused abrogation of the protective effects of nicotine against cisplatin-induced apoptosis in A549 cells whereas ablation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 levels had no effect. These studies suggest that exposure to nicotine might negatively impact the apoptotic potential of chemotherapeutic drugs and that survivin and XIAP play a key role in the antiapoptotic activity of nicotine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson D. H., Schiller J. H. Cancer Chemother. Biol. Response Modif. 2002;20:763–786. - PubMed
-
- Sekido Y., Fong K. M., Minna J. D. Annu. Rev. Med. 2003;54:73–87. - PubMed
-
- Minna J. D., Fong K., Zochbauer-Muller S., Gazdar A. F. Cancer J. 2002;8(Suppl. 1):S41–S46. - PubMed
-
- Wu X. H., Wang H. F., Liu Y. F., Lu X. Y., Wang J. J., Li K. Radiocarbon. 1997;39:293–297.
-
- Li X. S., Wang H. F., Wang X. Y., Liu Y. F., Li K., Lu X. Y., Wang J. J., Liu K. X., Guo Z. Y. Radiocarbon. 1996;38:347–353.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

