Requirement for SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex in Tat-mediated activation of the HIV-1 promoter
- PMID: 16601680
- PMCID: PMC1440843
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601074
Requirement for SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex in Tat-mediated activation of the HIV-1 promoter
Abstract
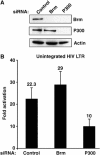
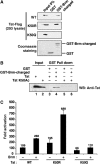
Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) promoter in infected cells requires the sequential recruitment of several cellular factors to facilitate the formation of a processive elongation complex. The nucleosomal reorganization of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat (LTR) observed upon Tat stimulation suggests that chromatin-remodeling complexes could play a role during this process. Here, we reported that Tat interacts directly with Brm, a DNA-dependent ATPase subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex, to activate the HIV-1 LTR. Inhibition of Brm via small interfering RNAs impaired Tat-mediated transactivation of an integrated HIV-1 promoter. Furthermore, Brm is recruited in vivo to the HIV-1 LTR in a Tat-dependent manner. Interestingly, we found that Tat/Brm interaction is regulated by Tat lysine 50 acetylation. These data show the requirement of Tat-mediated recruitment of SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex to HIV-1 promoter in the activation of the LTR.
Figures





References
-
- Armstrong JA, Bieker JJ, Emerson BM (1998) A SWI/SNF-related chromatin remodeling complex, E-RC1, is required for tissue-specific transcriptional regulation by EKLF in vitro. Cell 95: 93–104 - PubMed
-
- Benkirane M, Chun RF, Xiao H, Ogryzko VV, Howard BH, Nakatani Y, Jeang KT (1998) Activation of integrated provirus requires histone acetyltransferase. p300 and P/CAF are coactivators for HIV-1 Tat. J Biol Chem 273: 24898–24905 - PubMed
-
- Bochar DA, Wang L, Beniya H, Kinev A, Xue Y, Lane WS, Wang W, Kashanchi F, Shiekhattar R (2000) BRCA1 is associated with a human SWI/SNF-related complex: linking chromatin remodeling to breast cancer. Cell 102: 257–265 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

