Structure of complement factor H carboxyl-terminus reveals molecular basis of atypical haemolytic uremic syndrome
- PMID: 16601698
- PMCID: PMC1440827
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601052
Structure of complement factor H carboxyl-terminus reveals molecular basis of atypical haemolytic uremic syndrome
Abstract
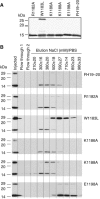
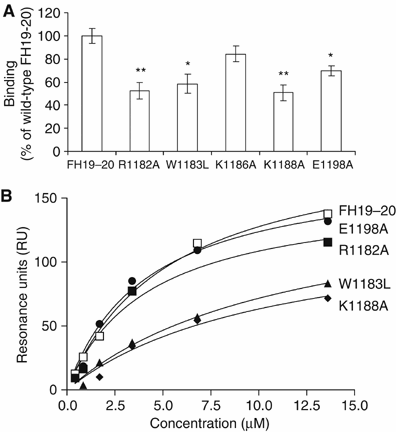
Factor H (FH) is the key regulator of the alternative pathway of complement. The carboxyl-terminal domains 19-20 of FH interact with the major opsonin C3b, glycosaminoglycans, and endothelial cells. Mutations within this area are associated with atypical haemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), a disease characterized by damage to endothelial cells, erythrocytes, and kidney glomeruli. The structure of recombinant FH19-20, solved at 1.8 A by X-ray crystallography, reveals that the short consensus repeat domain 20 contains, unusually, a short alpha-helix, and a patch of basic residues at its base. Most aHUS-associated mutations either destabilize the structure or cluster in a unique region on the surface of FH20. This region is close to, but distinct from, the primary heparin-binding patch of basic residues. By mutating five residues in this region, we show that it is involved, not in heparin, but in C3b binding. Therefore, the majority of the aHUS-associated mutations on the surface of FH19-20 interfere with the interaction between FH and C3b. This obviously leads to impaired control of complement attack on plasma-exposed cell surfaces in aHUS.
Figures
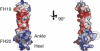
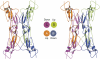


References
-
- Alitalo A, Meri T, Chen T, Lankinen H, Cheng ZZ, Jokiranta TS, Seppala IJ, Lahdenne P, Hefty PS, Akins DR, Meri S (2004) Lysine-dependent multipoint binding of the Borrelia burgdorferi virulence factor outer surface protein E to the C terminus of factor H. J Immunol 172: 6195–6201 - PubMed
-
- Aslam M, Perkins SJ (2001) Folded-back solution structure of monomeric factor H of human complement by synchrotron X-ray and neutron scattering, analytical ultracentrifugation and constrained molecular modelling. J Mol Biol 309: 1117–1138 - PubMed
-
- Barlow PN, Steinkasserer A, Norman DG, Kieffer B, Wiles AP, Sim RB, Campbell ID (1993) Solution structure of a pair of complement modules by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol 232: 268–284 - PubMed
-
- Blackmore TK, Hellwage J, Sadlon TA, Higgs N, Zipfel PF, Ward HM, Gordon DL (1998) Identification of the second heparin-binding domain in human complement factor H. J Immunol 160: 3342–3348 - PubMed
-
- Caprioli J, Bettinaglio P, Zipfel PF, Amadei B, Daina E, Gamba S, Skerka C, Marziliano N, Remuzzi G, Noris M (2001) The molecular basis of familial hemolytic uremic syndrome: mutation analysis of factor H gene reveals a hot spot in short consensus repeat 20. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 297–307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

