Short term culture of breast cancer tissues to study the activity of the anticancer drug taxol in an intact tumor environment
- PMID: 16603054
- PMCID: PMC1456977
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-86
Short term culture of breast cancer tissues to study the activity of the anticancer drug taxol in an intact tumor environment
Abstract
Background: Sensitivity of breast tumors to anticancer drugs depends upon dynamic interactions between epithelial tumor cells and their microenvironment including stromal cells and extracellular matrix. To study drug-sensitivity within different compartments of an individual tumor ex vivo, culture models directly established from fresh tumor tissues are absolutely essential.
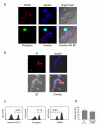
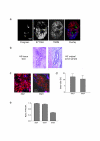
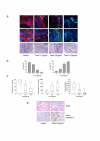
Methods: We prepared 0.2 mm thick tissue slices from freshly excised tumor samples and cultivated them individually in the presence or absence of taxol for 4 days. To visualize viability, cell death, and expression of surface molecules in different compartments of non-fixed primary breast cancer tissues we established a method based on confocal imaging using mitochondria- and DNA-selective dyes and fluorescent-conjugated antibodies. Proliferation and apoptosis was assessed by immunohistochemistry in sections from paraffin-embedded slices. Overall viability was also analyzed in homogenized tissue slices by a combined ATP/DNA quantification assay.
Results: We obtained a mean of 49 tissue slices from 22 breast cancer specimens allowing a wide range of experiments in each individual tumor. In our culture system, cells remained viable and proliferated for at least 4 days within their tissue environment. Viability of tissue slices decreased significantly in the presence of taxol in a dose-dependent manner. A three-color fluorescence viability assay enabled a rapid and authentic estimation of cell viability in the different tumor compartments within non-fixed tissue slices.
Conclusion: We describe a tissue culture method combined with a novel read out system for both tissue cultivation and rapid assessment of drug efficacy together with the simultaneous identification of different cell types within non-fixed breast cancer tissues. This method has potential significance for studying tumor responses to anticancer drugs in the complex environment of a primary cancer tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low radon doses sensitize MCF-7 human breast cancer cells to taxol.Oncol Rep. 2000 Sep-Oct;7(5):941-4. doi: 10.3892/or.7.5.941. Oncol Rep. 2000. PMID: 10948318
-
Pharmacological and small interference RNA-mediated inhibition of breast cancer-associated fatty acid synthase (oncogenic antigen-519) synergistically enhances Taxol (paclitaxel)-induced cytotoxicity.Int J Cancer. 2005 May 20;115(1):19-35. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20754. Int J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15657900
-
Paclitaxel Nanoparticles Induce Apoptosis and Regulate TXR1, CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 in Breast Cancer and Hepatoma Cells.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(13):1582-1591. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200504071530. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32364081
-
MicroRNA-16 sensitizes breast cancer cells to paclitaxel through suppression of IKBKB expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 26;7(17):23668-83. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8056. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26993770 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of flow and image cytometry for DNA content analysis of fresh and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue in breast carcinoma.Cytometry. 1995 Sep 15;22(3):181-9. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990220305. Cytometry. 1995. PMID: 8556949
Cited by
-
Short-term culture of tumour slices reveals the heterogeneous sensitivity of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to targeted therapies.BMC Cancer. 2016 Apr 16;16:273. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2318-x. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27085492 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing Patient Specificity in the Engineering of Tumor Models.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Sep 12;7:217. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00217. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31572718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-tumor activity of all-trans retinoic acid in gastric-cancer: gene-networks and molecular mechanisms.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 11;42(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02869-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37951921 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Secretase inhibition promotes cell death, Noxa upregulation, and sensitization to BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in human breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 15;14(3):R96. doi: 10.1186/bcr3214. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22703841 Free PMC article.
-
Using Tumor Explants for Imaging Mass Spectrometry Visualization of Unlabeled Peptides and Small Molecules.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018 May 17;9(7):768-772. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00091. eCollection 2018 Jul 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 30034616 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

